Global Star Party 167
Transcript:
well we're still waiting for the Florida students we are waiting for them that's
right the entire graduating
class or maybe ungraduated class class not sure but we want to thank fella terrenzi
for inviting them to
watch oh
we have a little bit of a schedule change here um Paul Cox from slooh is
sick and cannot make it tonight
so something's really going around guys
Mike Weezer's already on
and Don NAB nice to see you and John
Ray and hello to anyone else that's uh not chatting with us but watching
so and if you're watching this in uh replay you know welcome to the 167th
Global Star
[Music]
Party using NASA's James web Space Telescope a team of astrophysicists has
gained the longest most detailed Glimpse yet of the void that lurks in the middle of our galaxy they found that the
swirling dis of gas and dust orbiting the central super massive black hole called Sagittarius AAR is emitting a
constant stream of flares with no periods of rest using web's near cam the
near infrared camera to observe Sagittarius AAR for a total of 48 hours
and 8 to 10 hour increments across one year astronomers saw constantly Chang changing bubbling brightness and then
suddenly a big burst of brightness popped up then it calmed down again they couldn't find a pattern it appeared to
be random the activity profile of the black hole was new and exciting every time that the astronomers looked at it
while the team expected to see flares Sagittarius AAR was more active than they anticipated the observations
revealed ongoing fireworks of various brightnesses and durations the accretion disc surrounding the black hole
generated 5 to six big flares per day and several small subf flares are bursts
in between although astrophysicists do not yet fully understand the processes
at play they suspect two separate causes are responsible for the short bursts and
longer flares they believe that minor disturbances within the accretion disc
likely generate the faint flickers specifically turbulent fluctuations within the dis can compress plasma to
cause a temporary burst of radi radiation for the big bright flares astronomers think the cause is magnetic
reconnection events a process where two magnetic fields Collide releasing energy
in the form of accelerated particles traveling at velocities near the speed of light these particles emit bright
bursts of radiation these new findings could help physicists better understand the fundamental nature of black holes
how they interact with their surrounding environments and the Dynamics and evolution of our own Galactic home
well hello everyone this is Scott Roberts and David Levy and we are welcoming you to the 167th Global Star
Party um echo of the cosmos or Echoes from the cosmos uh of course everything uh you
know are made up of energy and waves uh and uh you know so you can think of echo
in any part of the spectrum uh you can think of cause and effect of uh you know
uh the evolution of stars and planets and even life itself um it has uh of
course literal and metaphorical meaning to us and uh we're glad that you're tuning in tonight uh I also want to
thank uh Dr pH arella terrenzi for inviting the students of Florida
International University to watch tonight um very happy that uh you're
here and I want to turn this over now to David Levy David thank you for uh coming
to Global Star Party well thank you Scott and it's wonderful to be here
today this has become quite a tradition to have these first they were weekly and
now they're like I say about three weeks or so and I really do look forward to
them I look forward to John's lecture about the astronomical
league and certainly to David's presentations that he does and
um mine uh I was going to do a real short poem today Oscar wild from Lady
wmr's fan no we're all in the gutter but some of us are looking at the
stars and that sounds pretty good but the poem that I wanted to read to you
today is a little bit different and I think I've read it to you before but
this is the poem that I wrote about oh about seven or eight months after my wife passed away I wrote this
in June of 2023 and it's called Wendy amongst the
Stars each day I awake today is the day I look towards her she is not there my
heart goes on but do I care will anything anything let in some Ray the
night is dark as dark it is dark as cold the sky is stars from west to east from
south to North just like a feast a pill Heaven Sent to calm my soul a telescope
stands stands and waits for my eye it ask just one brief look forward through
space like an open book and back through time open wide the gates I see a star
why is it there lapis philosophorum philosopher stone that strikes the night
it ushers me home as part of a pattern to learn I dare but Reason Not general
relativity gravity's geometry no Speck of thought no idea Works no system bot A
Spacetime crash to save its dignity she's a part of me a beam of light
amongst the stars in the sky a plant not there but there my soul enchant from
grief to Joy all through the night thank you Scotty and back to you okay all
right well uh we have um uh our next
speaker um is uh John Goss from the astronomical leag league and uh uh John
is uh um a staart at uh at the league uh
I don't know how many years he's been uh with with them but I think for over 20 years he's holding up 30 it looks like
25 or 35 anyways uh but uh very friendly
individual very knowledgeable individual and uh um always
um uh someone that we look forward to having on global star party I also look
forward to seeing U John's um uh
illustrations and presentations um I think he does most of the illustrations of star maps and uh
you know how to find things in the night sky um perhaps all of them and uh uh he
has a certain style which I really enjoy you know so um you know uh John thanks
for coming on to Global star party thank you Scott hopefully I won't
flounder around too much tonight no problem before I get started I want to say something to David you know that
that was a really nice a really nice poem and that might make a good preface mini microscope
in your next book you know I think people people would like seeing that it gives
something it gives an added touch to it all thank you John and you beat me to it
because I am working on my next book and I am going to include that poem in it
thanks for recommending it Johan well I'm sorry if I if I uh spoiled any secrets there but uh I thought it was a
good idea too um yeah thank you for having me on Scott yeah absolutely
and as you know from a lot of my talks I have something which I think is kind of planned and then at the last moment I change
things well okay that's okay we we'll see where I where I go with I think it
uh I was thinking about something this afternoon so I'll I'll try to start with it as soon as I let me see I can share
correct let me see can I should be able to share let's let's see about
this okay there we go well this isn't how I
intended to start but let's let's go head with this um I just wanted to give a little promo for two weeks from now on
August August see where I am on March 7th uh 7M
we have the next astronomically League live with Bob King who I think a lot of you know uh he's an excellent speaker
very knowledgeable always talks about something great and he's going to be talking about his his own personal perspectives of the night sky so uh try
to make your calendar free tune in to watch this either live or record it after afterwards it'll be it'll be
interesting okay this is not the title of my talk but this is how we're going to start mini microscopes
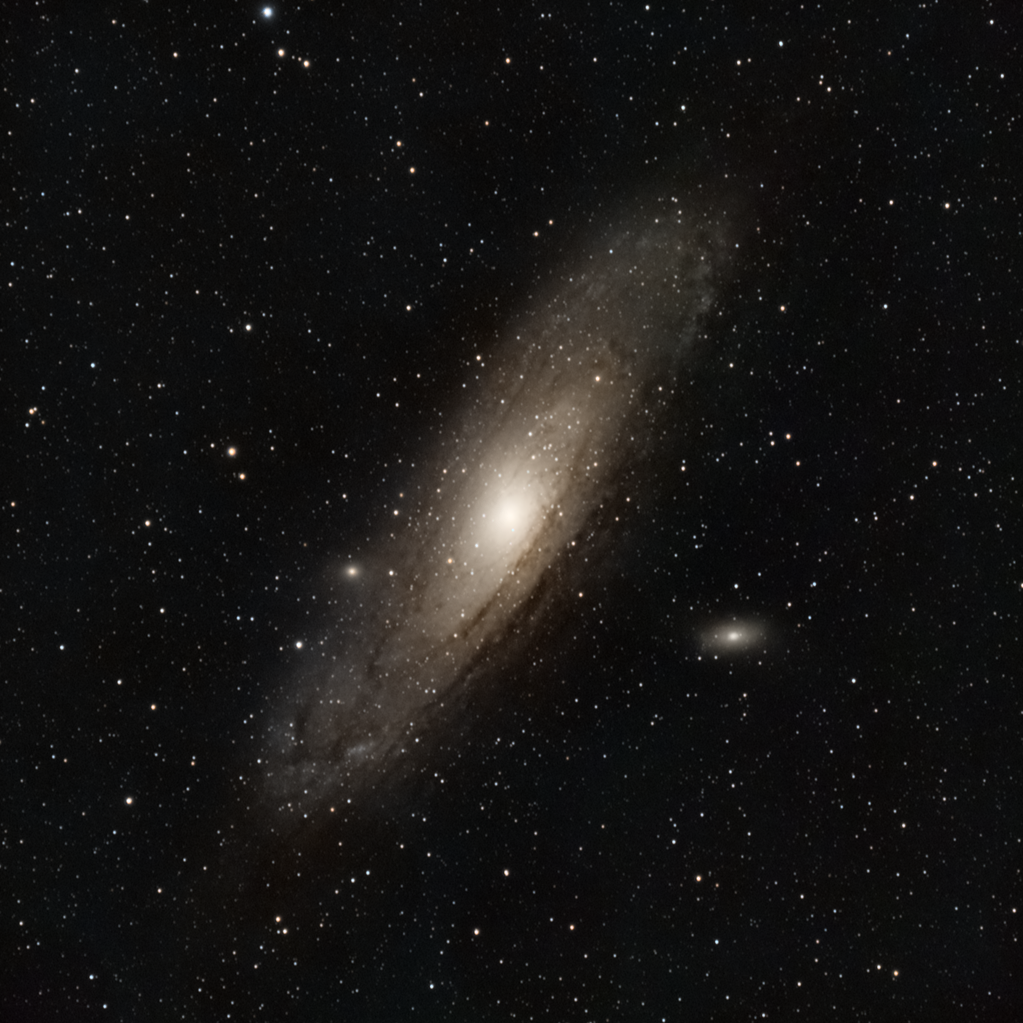
from the spectacular to the sublime now this picture needs no
introduction you all know what it is M31 the androm Galaxy A friend of mine Ed yast microscope
Dixon shot this and I saw it I thought you know that's that's a really really nice looking shot and I started looking
at it and I thought yeah that spiral galaxy you know M31 what's about 2.6 million light years away you know
150,000 or greater Lighty years diameter looks looks pretty cool uh H what else
can we tell on this well we we got some dust Lanes we're not seeing it an edge on but it's kind of getting towards that
way well what would a galaxy look like what would M31 look like if you could view it from high above it you at 90°
straight down either from its South Pole or its North Pole see what happens well I started thinking about that thought
well let's let's give it a try turn the um image
sideways and then stretch it and it'll give you a perspective that
so many of us don't have well none of us have but it would be pretty cool to see what the andral Galaxy would look like
from high above its North Galactic pole so what would that be well if we stretched it there you
go uh yeah you can kind of see the some spiral arms in it uh you can see off on photo of lice in hair microscope
the right hand side a bunch of dust Lanes but those are the dust lanes that we see because it's uh viewed at an
oblique angle but yeah it has a nice Center to it and you can kind of see some some uh dust Lanes in it spiral
galaxy it leavs me start thinking okay so here we are hovering above Andromeda and we want to turn back to our own
Galaxy what what would the Milky Way look like what would the Milky Way look like if we could view it uh high above
either the the the the the North Galactic Pole or the South Galactic pole well astronomers believe that this
particular Galaxy resembles our own pretty closely uh this is about 380
million light years away so it's nothing that you're really going to see it's not certainly not a showpiece in the sky
like like M31 is but it's something to consider you know we live in a bar spiral um with a number of spiral arms
coming out and what I would like to do is somehow or other segue this talk or severe dandruff big dandruff microscope
this introduction into my talk so this is what we're going to do I hope we're
going to zoom in deep inside this galaxy we're going to pretend it's our
own come in close we got uh in the circle there was our own little sun I
don't know if you can see it on your screen because I had to make it as dim as I could because in reality you probably wouldn't be able to see our sun
even from from this close distance off to its lower left is the
Orion Space and I put in three little belt Stars just to signify this that's Orion uh to the top of the screen would skeletal muscle microscope
be the Sagittarius section of the Milky Way so this is kind of our situation
here which we're on our home star and we're going to be looking at Orion and tonight I'd like to talk about
that constellation I don't want to talk about m42 we always do it's a great nebula some of the earliest fungi were microscopic
it's one of the coolest things to see in the sky uh binoculars small telescope
large telescope larger telescope still it is really good it gets better and better and better so I think a lot of when was the microscope
times when we look at Ryan we get we zoom in on that and forget about the rest of the constellation so I'd like to
point out uh um a few of the attractions that uh Stargazer can see either uned bbang microscope
eye binoculars and some sometimes with a small telescope so let's get started first thing I want to do is look at the
two belt stars on uh the the two bookend belt Stars left the eastern and the
Western U Belt Stars Delta orus and Zeta orus those are double stars and pretty cool to look out with
the small telescope pretty easy to see with binoculars it be be M much harder in fact it it's part of the astronomic
league binocular program binocular double star program it is interesting to
see um so that's a good good place to start off our little journey in Orion
you go from there this go to a place called colander 70 that we're going to be visiting Mr
colander a number of times uh in this this presentation it's a great binocular
star cluster it's a star cluster which we all have seen uh so many of us don't
really know what's there but it is it's a um I don't know it's it's I think it's
about 1,200 light years away about the same distance as all the other stuff in or the three belt stars are part of that
cluster and you can see okay zoom in on it yes there are a bunch of dim Stars cancels under microscope
around it there's more than a 100 binoculars a point them out um telescope
n not really because the field of view is too small but something like this is a great binar object so next time you're
out looking on Ryan and once something more to look at besides that guy down towards the bottom there m42 look at
this it's staring staring you right in the face and it's
there another one I like pointing out is another colander object
excuse me um the reason why I'm pointing this out is because Galileo tackled this one he described it he uh saw it one of darkfield microscope
the first objects he looked at through his telescope and the reason why he looked at it is because if if you look at this uh this this little two or three
stars you see up there with the uned eye if you have really good eyesight you'll be able to spot them but if your
eyesight isn't quite so good that it'll get kind of blurry and he wanted to look at it to prove that a lot of these fuzzy
objects in the sky blurry objects in the sky we really a glomeration of stars
including this one so looking through a small telescope or even Bish you'll be able to see it's dental microscope handheld
not just one two or three stars but it's a number of them and there's Galileo's depiction of it down there on the lower
right [Music] um I guess he wasn't really that great of an artist but uh I can kind of dental microscope hand held
picture some of those stars that that he got this is a an object for for you to look at tonight right at the at the top
of Orion it's called the Orion head nebula I believe General
discussions Orion also has uh variable Stars a nice carbon star RT or
rhus um it's something that you will have to really you can you can use binocular to to look at it and it varies
in brightness of I don't know how what's its period it's probably like 300 days but it's probably about half a magnitude
or a little bit more that it varies so keep an eye on that um and uh look at it
its variation and brightness yes but also look at its color try to try to note how that changes a little bit as depth of field microscope
time goes on as this period progresses so that's another object to look at and it's part of the astronomical carbon
star program you know the league has all these these different uh observing programs to help you um investigate the
nice guy because there is so much up there sometimes you go out and you go yeah let's look at Orion okay looks at
m42 great now what I don't know I'm all I know this is this too much so this
helps you find a lot lot of stuff it keeps things clear in in your mind all these lists there's another colonar
object and this is one that a lot of us has seen but we miss all the time uh
Coler 65 it's really easy to find it's a great bin archaeologic in fact the whole
thing fits inside one binocular field of view uh you look at the U U Bellatrix
which is the upper right hand star of Orion and you look above it to the to the to Beta orri uh which is a fair
easily seen star and about halfway between those two is this section of the sky am your binoculars at it and just
about every Star that you see in there will be part of this cluster it's a true cluster like all the other stuff on Ryan
it's it's 1,00 to 1200 1300 light years away but there are number stars in fact
to me it looks like it's it's an arrow pointing to the to the west but uh go ahead and give that of you after you uh
look at the the the uh excuse me the um the other excuse me other Coler object
go a little bit further north and look at 65 that's something to view a lot of people haven't seen it and it's easy to
find this is an interesting cluster which uh a lot of us have talked about in the past but I it Bears mentioning
again the uh I think it's called the 37 cluster NGC
2169 and 37 cluster because if you have some imagination you can see that it is
shaped kind of kind of like the number 37 kind of okay kind of it's also a
Callander object and I don't I don't think I have it it's a number in front of me call under 83 I think but um nice
one to look at anyway it's it's something to uh to to show your friends because it makes you look knowledgeable and gets them peering into the eyepiece
and they'll be saying I don't see to 37 or somebody will say yeah but it's upside down you know like gets the
conversation going you can talk about these things it's not hard to find in Orion
okay looking back at the constellation we we got a few more object um I'd like to run through a couple of them which uh
one of them isn't well you'll see we're going to zoom in no we're not headed to the Ryan nebula we're looking
at at number 42 and 45 orus these stars are they are not
related uh they're more what you call an optical double they're right next to each other they're about four arc
minutes apart which four arc minutes is typically said what a person with
average eyesight or or good average eyesight they to be able to see to split something like that so if you have good
eyesight and you're observing from a dark location try to look at these two stars and see if you can see two stars
they're fifth magnitude uh so they're they're not bright by any means but then
again uh if you're observing from a dark location you ought to be able to split them see if you can that is one way of
testing your eyesight some something to do it's right above the the the nebula and another thing which I I shouldn't
really say I like saying that it gets people's attention but I will say it uh
on sky and telescope's popular Sky pocket Sky outlas which I use all the time uh they made a mistake in listing
this and part of the reason why I'm bringing this up is because I didn't know that so I'm trying to find this thing all over the place and it's not
there not not in the listed spot check all these other references and bingo there it is it really isn't with
binoculars is certainly not not hard to find next we're going to go to Sigma
orionis um H what to say about this there are it's a multiple star
system for sure there are like six different components there may be a lot more uh it may be considered to be a
really small star cluster there are an um say another half dozen to a dozen
stars in the area which I thought that might be belong to it but through a telescope this is what you're going to see and the more you look the more stars
you're going to see because you can see some of those are actually very small double Stars close together um something
to keep in mind again in in the constellation Orion probably close to a thousand L years away you know part of
the whole nebula complex with all these Stars embedded in
it now this is an interesting one I can see I didn't put the name up
there this is called the Metro the metronome um asterism if you tilt it
sideways you can kind of picture the metronome tick tick tick back and forth
and it's easy to find it's one degree to the northwest of gamma orus uh these are about eighth magnitude
Stars so yeah in binoculars you'd be able to see it telescope would be a little bit better but this is they
aren't related this is just somebody who said hey this this looks pretty cool I
I'm going to make a note of this and there it is uh the metronome asterism
it's part of the astronomic league asterism program it's one of the ones you can see easy to
find I think this might be my last one this is NGC
1662 a cluster uh very sparse not much to it uh and I'm I kind of putting it on
there because I let you know that it's another colander object and I can't remember which what it's called Coler
55 and uh this is Sigma orus to me looks a lot better
than this thing does but uh it's another object up there you can go ahead and try try and give give it a good shot so all
these things in the night sky you know you look at the m42 great what do you do
after that we try to find some some of these other targets as well um as you can see I have what six seven eight nine
10 10 of these things up there and I missed a few uh kind of on purpose because I think I'm I'm running out of
my schedule time here but I wanted to make sure that I could cover all this stuff so when you're out with Orion look
at m42 then go on to some of this other stuff and you're going to come out with a much better appreciation of what the
sky offers especially what this particular constellation offers and good luck happy observing thank
you okay so um did we talk a little bit
about uh the um Rice Canyon event I have not said
anything about that because I thought we might let's remind our viewers about astrocon are there any spots left at all
or yes um there are okay there are um but they I say we say this every time
you better do it quickly because they're going fast uh most you know most conventions we we hold um hold in June
or July and there are a lot of spots available in may but uh with this one I
think they're all going to be full uh probably by the end of March so if you want to go you know put it on your
calendar and start investigating it uh and try to get get your spots now really with the the
limitations uh is really uh one of accommodations we have uh the hotel
accommodations which is at Ruby's in and Lodge that has a few hundred rooms we have camping uh we have both uh
recreational RV camping and primitive camping but still once those spots are all full
there's no no place to put anybody so that's that's when registration closes
go ahead and take take a look at at the schedule and all that because you'll find that there are a lot of great workshops
um disguiser are fantastic workshops in the day in the evening uh you'll meet a
bunch of people you get to go out and observe with them um you'll have you'll have a good time you'll have a great
time you'll meet the dark Rangers you'll meet uh you know some amazing people and
make some new friends you know I do that every time I go to uh astrocon but this one's called uh as it's called Aston
it's called astrocon Aston normally it's called Alcon that's right yeah normally it's Alcon but this is called Aston
because we have 19 vendors maybe it's 18 vendors
wow maybe it's 17 but it's it's one of those so there you know should be a
bunch of uh places for you to look at sure uh you know products and stuff and I I know you know Scott will agree agree
with me on this this is a great place to come and sort of Kick the tires you know you have a telescope or eyepieces or
finder Scopes or Star Maps or programs or clothing or whatever you know you get
to see it before you buy it if you don't like it okay you move on but uh it'll be worth your time I know you worth your
time absolutely all right well John thank you very much thank you
um uh our schedules juggled here a little bit uh Sak was uh due to appear
on next but uh we're going to move on to David Iker who's just getting back from
the iHeart Pluto festival and uh I think he brought some props with him so that's
kind of cool and I wish I had gone but uh maybe next time David you'll have to
come next time it was great uh fun and I've heard about it for a number of years I've been involved with LOL there
for quite a while oh yeah the board but I have not been to the iHeart Pluto Festival until this year it happened
about a little more than a week ago now because it has conflicted with the astronomy Magazine Star party that we've
done in Tucson for some years so this time I way Michael paid attention to
things here and uh ended up uh hosting the main session of the iHeart Pluto
Festival so I thought I'd talk a little bit about what happened uh a week uh and and a little change ago in Flagstaff
right now I'll say something about the loal observatory staff and Pluto they know it's a planet okay
right well I'll talk about I mean Alan stern was there and and some of our friends who uh think that it was proper
for Pluto to be demoted started discussing that with Allan let me just
cut to the Chase and say Alan pretty well put them into their place there with the argument there
so astronomers at the IU in charge of planetary science decisions is the short
version of that a short answer yeah yeah okay I'm gonna let you take it from here
thanks Scott so I'll share my screen it was about a a week and almost a week and
a half ago now that we uh experienced our f i experienced the my first IH
heart PL to Festival but this is now a an annual event uh in Flagstaff so let
me share my screen and I will attempt to share the right thing that'll make it
more more proper um and can you see that yes on your screen and in that case
if you can I'll start a slideshow and just talk a little bit about what happened there and I was really uh
privileged to be there with some old friends uh who was there to speak about uh Pluto
and his biography of Clyde Tomball of course the biographer of Clyde Clyde was
our old friend uh more so with David knowing him very well uh but we both
hung out with him quite a bit in the later years of his life and he was something else I'll I'll ask David maybe
in a few minutes here to recite his favorite uh Clyde joke that this is a
joke that Clyde told he Clyde would rattle off a joke a pun about once every
two minutes for an entire evening at a time you know it was absolutely unbelievable most of them were Crow
related jokes too um puns rather so he was something else uh and and David
being there I think at the festival I think you had a really really good time oh yeah David and Alan Stern our other
buddy there who was of course the principal investigator of the New Horizon space craft that flew past Pluto
in 2015 and gave us our first uh clear understanding of the Pluto system and
it's many it's large Moon Sheron and it's uh several other moons as well then
we had a special guest there as well uh Adam nemoy who's the son of Leonard
nemoy so we we got Star Trek in the mix there and some amazing stories that I'll
mention uh from Adam about Star Trek about fandm about Hollywood about his
father about all kinds of things that we're really fascinating to hear about so this happened about a week and a half
ago for a few days and will happen again next February it's nominally held on
February 18th uh the Pluto Discovery anniversary date but only when it really
lines up with a good weekend well which was a little earlier than the 18th this year but it was a lot of fun and we had
a great time and a great crowd and uh just to talk talk very
quickly about this probably stuff I already just talked about here uh but it took place uh the 13th uh and and a few
days thereafter um in Flagstaff the main event the the talk that we had we had
quite a number of politicians there the mayor of Flagstaff and a uh an Arizona
representative who's turning into a pal who's very very pro- astronomy and and
helping to get a number of astronomical projects done um and and uh of course
David and Allan and Adam and I um so so the politicians talked for about oh half
an hour 45 minutes then I think the four of us had about 90 minutes or so to talk about all things Pluto and we also
talked of course about Comet Shaker leaving nine uh with David being there and and we had great questions that went
on and on from the audience and it was really cool because I had never been inside this theater which now really
host concerts but the Orum theater in Flagstaff which really is just down Mars
Hill into the base of the town there not very far from L Observatory that's where
Clyde went uh the night after he discovered Pluto and and realized that
that is what he had found and he went down and saw Gary Cooper in the Virginia
in this theater that evening so it's really you can kind of feel the aura of
Clyde in that theater just as you can of course staying in the so-called apartment in the slier building up on
the hill where Clyde lived when he discovered Pluto as
well so as I mentioned we had a great panel discussion that went on for a long long time and it was David and everyone
else uh there were they were fantastic just talking about everything you know
all sorts of incredible memories uh about Pluto about Clyde about things that Clyde said and how he felt about
things the New Horizon's Mission and of course Adam uh with Star Trek and his
Recollections of his father uh and so we had a really good crowd there of I guess
a couple hundred people or so maybe um in the theater there and a really good time and that wasn't the only event that
happened that constituted the iHeart Pluto Festival we also had tours of L
Observatory going on all the facilities there uh Talks by Adam uh and others he
talked uh uh about his father of course and uh talked about a book that I will
show in a moment here that he wrote of reminiscences and he showed a film that
actually came out in 2016 that he produced uh late in
Leonard's life uh um about his father and about Star Trek that that is a
fantastic uh film that you can find on um Amazon Prime if you'd like to see it
we also had the unveiling of a new beer the mother I think I'm allowed to talk
about this Scott on this is this is a a grownup program here th this is uh uh
unveiled by Mother Road Brewing Brew brewing in Flagstaff this year is boldly
go which incorporates as you might be able to see persal L the New Horizon space CFT the title for Star Trek
everything we had going on there this year is in this beer which is a fairly High powerered
IPA and you can get that along with many other astronomically themed beers uh
from mother Road brewing in Flagstaff we had a pub crawl then and an astronomy on
tap trivia contest uh that a bunch of the L astronomers uh ran there that was
great fun we had observing up on the Hill of course uh uh the round table
discussion that I mentioned and the film and um a talk by Adam an interview talk
by Adam that was sort of conducted by our friend Melissa as well so it was a
tremendous uh more or less three-day event there that went on that was just a
a heck of a lot of fun so I I think if you can go to this some year you will really enjoy talking about Pluto um and
uh you'll find that many of the people there uh maybe not surprisingly feel that Pluto is a planet despite the IU in
2008 so this is a shot in the theater of the four of us up there talking on for
our uh discussion and one thing you know I've known David and Allan since I was a
teenager essentially uh so you know I know them pretty well and we had a great great discussion about everything
they've been involved with it was neat to uh meet Adam who's a pal now and find out everything he's doing he's been an
attorney and then uh sort of turned into being a director in Hollywood and directed a bunch of uh drama programs
and and also some movies as well really interesting guy and I'll talk a little bit more about his life history that is
quite interesting in in a moment here but it was quite special for me to hear you know what are his favorite Star Trek
episodes was one question question we had for him and I was really pleased that one of the few that he mentioned
that he thought was really special is the trekkies will recognize this is the managerie that two-part early uh sort of
redone uh um uh sort of pilot if you will um that came after the original
pilot the cage so he that was a favorite of his among others and uh so we talked
a lot of Star Trek as well there has been a Changing of the
Guard at L observatory in a very exciting time Jeff Hall now has retired
as director after many years of great success Amanda Bosch great uh astronomer
and friend is now the director of L Observatory you may have heard this but several months ago at L we inaugurated a
huge $55 million new Museum astronomical Discovery Center there that is going
gang busters there uh in addition to all of the history that happens on Mars Hill
and the large telescope that I'll show in a minute that is a very Cutting Edge instrument uh that's down at Happy Jack
about 20 miles outside of Flagstaff that's doing a lot of cutting edge stuff
so things are really rocking at LOL Observatory it's sort of a golden era
now there for all of us this is the 4.3 meter it's now called
the L discovery teles scope uh it represents really The Cutting Edge research everything from solar system
stuff uh all the way to very distant galaxies and some cosmology so this is somewhat rare among large telescopes uh
at research institutions that quite a number of users are employing it from
various places not just L Observatory and it's really doing research all across the gamut of astronomy from the
solar system to the very distant Universe which is a little bit unusual but it's a magnificent telescope as you
can see uh we also have LOL and its history of course that it's very famous
for there I was a little bit uh startled at first I think it's fair to say uh
seeing the new ADC the gigantic multi-million dollar Museum there um
without many artifacts in it and I think having considered it it's best to have the artifacts where they are in the uh
in the archives if you will and the and the library there and much of the museum
is really focused on astronomical knowledge with displays with video screens with huge areas for the kids to
learn about astronomy and uh we had I think 1500 people there the first day uh
a week and a half ago there on the weekend and that was a really busy day there of course the two great historic
instruments are reunited now for some years on the hill 24in Clark that was
made famous of course by persal LOL and his interest in Mars originally chiefly
and very famous in 1912 of course with the slier spectrograph mounted on this
telescope and the discovery by vestos slier that the Universe uh that that
many many objects I will say are moving rapidly apart from each other which
pre-aged hubbles a confirmation of the expanding Universe at the nature of
galaxies as independent very distant bodies of many many uh
stars and um The Cosmic distance scale which is much larger than anyone of
course in the 191 or the 1920s uh imagined it would be that's on the left
there and then uh it was out at Anderson Mesa for a number of years but now the
so-called Pluto camera 13-in astrograph with which Clyde discovered Pluto is
back on Mars Hill the original Dome site there um and this is also an instrument
that our pal Brian skiff was the last major user on for many years uh taking
uh several times as many observations as Clyde did with this telescope so Brian
knows this telescope very very well and you can see that on the end of the counterweight bar on this telescope is
the fa famous boxing glove uh in red there uh placed there so you don't Bop
your head on something sharp in the middle of the night so these are the two primary very historic instruments of
course that are at L on Mars Hill above Flagstaff
today just remember uh Uncle Percy wants you to volunteer at l i we saw this in
in one of the buildings and I had to take a picture of this this is priceless whoever made this I don't know but it's
that's good stuff um and uh there now is
uh all you need to remember about Adam nemoy are good New Pal live long and
prosper and you know that's the sign to to wave their great great guy and this
book that he wrote is one of a couple of books that he's written but this is the Memoir about his father and it's a bit
of an an involved story but uh Leonard was really struggling in the early 1960s
as an actor um had come uh uh all the way across the country and didn't have
that kind of uh um connection happening in Hollywood so he did most of his early
acting jobs lasted about two weeks and he did all sorts of other jobs to get uh
the family through months to months in those early days they included things
like working on uh laying bricks in Gardens of the backyards of houses in
Hollywood uh they included installing repairing cleaning and setting up
aquariums in fancy houses in Hollywood anything that he could do he did a lot
of jobs and he he was a tough guy and a guy who uh worked really hard for the
money that he had um and and a pretty old school guy Leonard um in many
respects now when Star Trek Struck it was a big success almost right away
although you know it really garnered its Legends in reruns later but it was a
success uh for quite a while there with Paramount and by accident a couple of
fan magazines published the Nemo's home address and telephone number in
Publications so suddenly the Nemo were besieged by people coming to their house
they had a mail truck after not long delivering an entire truck of fan mail
to their house right away it was an overwhelming situation that really kind of spiraled out of control for this
young kid Adam who was growing up at the time very young boy so uh Leonard was busy he was uh
away most of the time working on the series he was at home in the evenings working diligently on learning his lines
with his wife then he crashed and he went off and did it again and he was a rare guy around the house in those early
days working so hard on the series he also eventually and and Adam was was
incredibly open about this kind of thing and everything that that he's gone through in his life and uh talking about
it with others Leonard eventually became an alcoholic Adam sort of rebelled um
being you know sort of hanging out with guys who his father didn't approve of
And he as he tells it started a 30-year career smoking marijuana so there was a
great distance between uh Leonard and his son Adam for many many years um a
difficult uh strained relationship they got back reconciled and had a great very
close relationship for the last years of Leonard's life and and that and worked
on this documentary uh film about Spock which you can see so it's a really interesting
story um and this is a really interesting book if you get a chance to read this which is his moir of his
father so great guy great pal remember there is a boldly go beer kids stay away
from this it's powerful stuff we don't want to be a bad influence wait till you're old um when you're old you can
get away with anything back you and and this book is really entertaining as well
and that is really the experience of this year's ihart Pluto Festival which I
hardly recommend if you can get to this in the future it's a really good and unique time and I think we'll be having
some of these folks back talking about Pluto and comets and Star Trek and all
that good stuff in the future so thanks very much Scott thank
you um the uh uh the comment about um uh
lner nemoy becoming an alcoholic is uh is a surprise to me you know of course I
think it probably is to a lot of people um but uh you know the pressures of of
doing something like that are enormous and um you know I can
understand how someone might uh take refuge and something like that so it's
uh it's uh tough and um uh but it looks like uh eventually he uh prevailed and
um you know was able to reconcile and all of those things so that's that's all
good and uh the title the most human now now I get it you know it's like what
what a strange title for Leonard nemoy you know so yeah yeah yeah think that
maybe he might have carried over that logical uh thinking Persona over into
his real life I don't know if that and he was a very AER serious got you know
you I mean Adam talked about this at Great length a little bit on stage and a lot with us hanging out you know he he
he would be you know you know pretty much similar to that you know cold
analytical character if you will of Spock so so this is what you think came natural to him I guess do with your life
is hanging out with these guys and and smoking pot where do you think that's that's going to get you young man kind
of that so that I mean that's that's that's how it was you know how it was
and that was a revelation to me as well yeah yeah dve David Levy I I've been at
David Levy's uh home a number of times and there's a photograph of uh Leonard
nemoy with David uh you met you knew uh Leonard nemoy is that right David yes I
did I I knew I knew lonard I met him Carolyn and I met him when he was at LEL
number of years ago and uh I really enjoyed meeting that
man and um I love the two books that he wrote I am not Spock and then I am
Spar and uh they're both so appropriate because I think it was after the second
movie where Spar actually dies that neore decides he is Spar and I think that really pretty
pretty definite I wanted to point out that I'm having a lot of difficulty with your
audio today oh and I don't I'm not sure how long I'll be able to stay on but uh
but I will I will do my best okay all right well that's fine um up next we're
going to have uh uh Miracle Marcel um he
is an astronomer and astronomy educator from Africa and uh he is um he prepared
a uh video for us uh so that we could get uh you know a good transmission uh
from his program and so Mira Miracle marel here we
are hello my name is miru marel I am the founder and the director of the largest
citizen science community in Africa called The panafrican Citizen science
EAB so in this in this program I'm going to be
talking about our project um and our achievement over the
past three years so in table of content I will be
introducing pasab our key project and our results so pasab was founded in December
4th 20120 and our aim is to promote hands on activities in astronomy and space
science through citizen science and soft astronomy research in Africa as a means of advancing space exploration and
enhancing space education and Outreach so and how we do that is by collaborating with entities in the
global North and bringing those opportunities to Africa and all our
activities are online all our activities are based online so here is your
official logo showing the map of Africa here you can see individuals with their
computers or phones are analyzing and reducing space data and that is exactly
what we do we also have a WhatsApp group where we interact uh within our
community so for the general requirement all par project are suitable for all
individuals regardless of Age religion country sexual orientation academic or
professional affiliations levels Etc so to participate in our project what we
just need is to H have a basic knowledge of computers most especially uh Windows
operating system internet and passion for space now in our organization we have uh
we have different kinds of project classified as primary project and secondary project the primary project
are our main project and I'm going to be describing them one after the other so the first of our primary
project is the panafrican asarch campaign and we collaborate with the international astronomic resarch
collaboration we are their biggest partner in Africa and in this project we contribute
in in in planetary defense through discovering new asteroids we submit the
report to the minor planet center so that the orbit of this asteroids can be
classified and continuous monitoring can be done in order to avoid events like
this we use the astrometric software to analyze the images here you can see
there are about four images taken at different time intervals here is the blinking windows
that blinks images in order for you to see if an object is moving or not that
is how we detect Aston words the data we use are gotten from
the pen stars located at the University of Hawaii and the Catalina Sky Ser
located at the University of of AR Arizona now in this chart there are uh
there are more surveys around the world observing the sky scanning the sky and
taking data asteroid data but these two are the the are the most they collect
the most asteroid data and now they have automated system in them that detect
this asteroid but not all of these uh not not all of these asteroid are detected so they send the
data uh those data uh to the international Asic resarch collaboration
so that we can use uh the manpower to discover this asteroids so we are part
of them the panafrican asteroid search campaign and here we engage different
entities across Africa in the asteroid search campaign so here is just one of
our groups the amateur uh amateur astronomy Libya so this is where the
teams we download the data analyze the data submit it through here so this is
just the
demonstration so for the tools to to participate in the asteroid search um
our participants would need Windows operating system internet and astrometric astrometric is a free
software now in training we have recorded videos in English uh French and
Arabic and here is just an example of one of the one of my recordings in English we also have Arabic and French
we have some of our our members volunteer and develop those videos in
other languages too we also conduct online training via
Zoom so far we have discovered 32 asteroids and those those asteroid were
discovered by about 60 of our citizen scientists however however we still have
about we see have hundreds of preliminary discoveries that are yet to be
confirmed so here is the the academic calendar for the for the new Academic
Year which started this August it runs every month till May that is how we
conduct it every year so here it say the second uh our
second project exoplanet and photometry and we collaborate with NASA exoplanet
watch So In This research we contribute
data we contribute data in order to refine the mid Transit period of already
discovered exoplanet in order for the future missions like the James W Space
Telescope to study them again and you know in details in order to to to detect if there is life or no life in them but
the reason why we are doing this is because um when these exoplanets were discovered by the Kepler and the test
missions their periods were not accurate so are actually redefining the M Transit
time in order to improve their period so we we reduce we reduce the data with
exotic software to produce this light curve and after that we submit the
report to the American Association of variable star observers to participate in this project
we have three sources of data through the exoplanet watch website you can request
data directly from NASA they would give you a data if you submit your email
there we also have access to the micro Observatory there you can schedule your
own missions or can can observe Stars okay using the micro
Observatory so this is the process of scheduling and after requesting it the
micro Observatory is going to turn around to focus on that spot we also use
the L com Observatory for observation we are part of the global Sky partners of
the L com L com Observatory we have about 100 hours of observation time for
our research and other endeavors also so the tools for This research any
operating system internet Gmail Gmail not email because this exotic program is
a Python program and it is mounted on Google collab so to be able to have
access to it you need a Gmail and all the software is online for the training
methodology we have recorded videos I also offer online training via zoom and here's an example of the recorded
video so in this project our aim is to
make our citizen scientists to to contribute to peer reviewed publication
in order to enhance the academic and professional status but being citizen scientist they
do not have advanced level of of astronomy in order in order to carry out
professional astronomy research so we sought for some research they can do
without advanced knowledge of astronomy and one of them is on double star research we collaborate with Dr Richard
freed the president of the institute for student astronomical research in the United States and in this research what
we do is to um to update the position angle and the
separation of of these double Stars we also conduct uh verify if there are
binary stars or Optical double Stars so the student write papers they write manuscripts on their findings and submit
to the general of double star observation so far we have written since this year 2024 we started here we have
written up to 12 manuscripts but four have been
published so in the trading methodology we have recorded video like this and
online interaction with the research instructor for the tools you can use any
operating system you would need internet you need as IM and other
programs then we have radio contact to ISS with amateur radio on the
International Space Station this opportunity is going to allow our
African African citizen scientist to interact with astronaut AB International
Space Station in order to ask them questions this is a project that is usually a seen in advanced countries
however entities in South Africa and Morocco also conduct this exercise but
we are the first organization that is going to bring it in the African society
and we hope to make it permanent so here is uh an ai ai generated image of how the event
is going to be the students are going to interact with astronaut via zoom and we are getting prepar to conduct this
starting from 2025 so in the AST photo visual
development we teach our citizen scientists how to process space images
to produce colorful visuals so we teach them how to process
images from the Hubble Space Telescope the James West the James W Space Telescope and the last coms
Observatory so for the Training Method methodology we have recorded videos we have online training via Zoom we have
Photoshop training uh we have game so in our telescope giveaway
program we collab collaborate with GNP gred and aers in distributing telescope
across Africa and the purpose of doing this is because we are working with a
whole lot of teachers across Africa and some of them they need this telescope
for their teachers training program so we collaborate with this organization to
distribute telescopes to them another another purpose of this telescope giveaway is that there are
some countries in Africa with find it so difficult to recruit citizen scientist so it means that the astronomy knowledge
in those places are very low so when we find somebody from that from that place
we give that person telescope for astronomy Outreach in order to spread astronomy and also to recruit citizen
scientist life observation life observation via web uh
via Sloop web telescope so we use the Sloop telescope
for Life observation here is the Dome we use it to observe the
moon the son life okay life observation
not through email life observation we can also use it to observe deep space
images and most importantly we use it to observe eclipses like this are this is
the pictures of these are the pictures from the eclipse that happen in North America
uh in April of this year we we're observing it right from Africa while it
is happening in America so here is the map of the world showing the different places in the
world where the slow telescope is located so they have location in Chile they have location in Canary Ireland and
they also have location in Australia they also have mobile telescope they move around the world for Eclipse
observations so in order to evaluate our result we issued surveys to our group leaders in
order to know how they are adopting our project in their classroom so from the
survey we we we got that 691 citizen scientists have been have
been engaged across 45 45 countries in Africa mind you there are about 54
countries in Africa so 45 out of 54 um countries have been engaged now we
have about 70 groups we work in groups we don't work individual we work with groups now out of those 70 groups we we
classify them according to levels for instance a is equal to 15 a represent um
National Space agencies National astronomic societies National observatories and other National
entities B is equals to 25 representing University groups and C is equals to 30
representing private astronomy organizations and also including secondary
schools so here is the gender identities most of the people that feel the surveys
identified as male and female levels of Education we have secondary schools we
have Bachelors we have Masters we have phds so from here you can see that Bachelors have the most
participation and for this PhD the phds are mostly University researchers and
lecturers are adopting our project in the classroom and engaging these
students so uh our Parc project the four active
ones from the survey we discover that the asteroid search is the most
pronounced although uh others recently Incorporated them however the asteroid
search has been with us since the past 3 years so here is the year of participation of Citizen scientist
we started this program in 2020 and the number we keep in recruiting um people
number have been increasing every year every year by year and we are in
2024 so there are five geographical zones in Africa so here are the
population of Citizen scientists from each of these geographical zones so here
is the map of Africa showing uh the countries where we have expand our Network the countries in blue are the
countries have expanded our Network we are looking for participant from Mali from morania and K and other
countries so our project has been contributing to six out
of the 17 um sdg goals sustained development
goals which are quality education gender equality decent n work and and economic
growth gender inequality uh reduce inequality uh peace Justice and strong
institution partnership for the goals so we have written papers on our
about our organization and also we are writing papers on each of our projects so so far we have written two and we are
still writing more so if you want to read everything about our organization and have just explained now I want you
to go to our website and go to the publication page so that anytime we drop
any paper there you can have a look at it you can also sign up for newsletter so that you can receive notification
when the papers are ready they are still undergoing peer review so we are looking for collaborators across Africa and
Beyond we are looking for collaborators so if you are interested in collaborating with us please reach out
to us thank you so
much and thank you uh Miracle uh for that
presentation um he is uh he is an astrophysicist and uh um probably
leading the largest citizen science program for youth in Africa uh covering
spanning over 54 countries so um really a a a great um uh you know force in uh
in citizen science today our next program is with uh Adrien
Bradley Adrien is uh someone shares his
uh vision and his photographic Talent uh for night sky
photography uh and we always enjoy having Adrien on thank you so much for being on the 167th Global star party I
think you probably are getting close to having about a hundred Global star parties under your belt at this yeah I
think so I'm seeing uh in Facebook I'm seeing
three years ago or four years ago and there's a picture of my face the global
star party I'm gonna have to send you a new one Scott because I got more beard now so oh you got more beard now okay
yeah I gotta yeah I've been beard has been growing as long as I've been getting on global star party so for some
reason I can't grow a beard I it'll grow like right off to the side but that's it you know so I fig just growing off this
side that's not cool so well and you know what it'll be cool again in 10 years um even the New York Yankees um
for those that hear about sports I know Daniel's over there waiting in the wings from New York um relax their uh rule on
Clon shaven you'd be able to play for the Yankees but uh they've relaxed it so
that's some of the the trends that we have you know in society bearded bearded
men has become a trend and so they well groomed beards um are now allowed and and it may
a few players have uh you know wanted to be you know on the Yanks and sure it was
really I they prevented but uh as astronomers out there yeah as astronomers out there you
all probably aren't as concerned about the Beards or baseball some of you are yeah that's right but uh you know we we
look up so what I'll do Scott is I'll uh I'll share one of my screens let you
have this and what I decided to do is um show a picture here there's a few
things with this picture that I wanted to share not only um love of the cosmos
but um love of um the Imaging that I like to do of the cosmos and so you
should be able to see it now um yeah it's slightly off color but
everything about this picture um describes a few things from
this tiny reddish dot here is actually the uh lunar eclipsed moon we have a
lunar eclipse coming and it's going to be at a similar time that I took this
picture this is um this was a little late it was later in the night um we're
going from Midnight the start of um the total lunar eclipse on March
14th um March 13th it officially starts at certain places but March 14th
totality happens somewhere between 2: am and 3:00 a. um now during this this was November
8th this was on my birthday in 2022 and what I'm going to do is switch
to an image you may be looking at it and saying well the Moon looks about the
right color everything else is sort of pinkish this is what you have when you're um you know your your colors
aren't quite as um accurate in your processing you want things the way that you look up
and that you see them and this is a little closer to it you've got your moon
Sky glow is everywhere around Brian is right here um that's serious and Canis
Major um Scott I believe this was Jupiter I would need to look this up again but I believe we had Jupiter still
in the um winter hexagon two years ago
it's drifted down to too it's drifted down in our skies to here um and I do
actually have a more current picture but then you have and
Uncharted I think more more of us that like to do images like this ought to
really try and shoot at this part of the Milky Way it's a challenge it's uh you've got the rosette here a lot of the
Imaging focuses more on Orion and brightening some of the reddish areas
here but um getting this part of the Milky Way is it is indeed a challenge
and um I think it's one worth going after and and it can be surprising to
see in this wide angle photo of this Lake it's actually called upon Pond but
it's trust me it's a lake um it can be surprising to see the moon
this little but this is the proper aspect compared to the entire night sky
now we see the moon and we'll see how quickly this comes up when we look up at
the Moon we see it a little bit bigger in our sky and this is I use Lightroom classic still to do a lot of my
processing of images in the cosmos so here you've got a picture that I took of
the totally eclipsed lunar moon Uranus is this
bright um looks like a star but this was actually the planet Uranus here and um
during a total lunar eclipse you see the Moon and it's normally bright enough to cast
the light and wash all of these stars out you get to see those Stars around
the lunar eclipse moon depending on how you take the picture um you can capture how that
looks it's it while it's eclipsed it's sitting there hanging in space you know
kind of in the middle of the cosmos so to speak um it actually looks if we go with this this makes it
even this is an even smaller image but I didn't uh let's see what happens if I we
go highlights all the Stars start to show up so it depends on the exposure you use a quicker exposure does not do
it very much Justice and then looking at it in
relation to this is actually this is one of the uh Raw photos that I took um
trying to capture it's a composite I tried to make because you can see this ring let's see if there's
a of this was uh this is me trying to capture that image with a with an actual
photo as daylight was coming in the moon was beginning to get out of Earth's
shadows still bright compared to the other stars and of course Stars aren't
round when you're out capturing the COS most and you're looking at it um and
sometimes you just want to look up at the uh night sky and you try and capture
what you see and that was the basis behind the images that I took here I
think this is another version of that image little off color and see this was the this was the image for the sky and
you can see the the color of that lunar eclipsed moon it washes out so
composits and a little bit of magic are done to get a final
image that resembles what the human eye some of what the human eye can see and
some of makes a certain things brighter that the human eye cannot see if this ever loads
it'll it won't be as pixel yeah here we go so some of what the human eye can see
and some of what's really there that the human eye might not be able to make out and that's
that's always my focus for that and so they rather than simply focusing
sometimes on just the big picture if you will
um of the uh and this limb coming where it's not totally this is maybe 97%
eclipsed here and I still took the photo of it um and then tried to process it
but rather than just focusing I think on the um you know the tight shots of
things in space sometimes I think it's it's a great idea to uh you know widen out a
little bit and this is of course you don't always take the perfect picture in
the first shot so the theme was the theme was about the um you know the
cosmos and you know how it makes feel and part of the part of the theme was is
those of us who um love doing night photography like this where
we're taking pictures of the night sky we're looking to process those pictures
to show what the cosmos looks like from our vantage point on Earth um I haven't
had a lot of opportunity to do a lot of Imaging of
the cosmos but it is something I enjoy and once
again I decided to take an image and just look and look up once we finally
got a clear sky now you're going to see to the bottom right of this
image um this was a longer exposure with not with my um camera that's modified
but with a stop camera and a fast lens
and I got to 125 seconds before I realized the long exposure I wanted to
take here was going to have to be interrupted because the clouds came to shut down the sky I had about I did a
stack of 40 images and I'll show you one of those images I'll show you what I'm
working on uh before we go to the next presentation Scott I'm working on trees
and one of the toughest things to do when showing how the sky looks is keeping the
trees looking as natural as possible stacking images is a great way to do
that but when you're in an area that's not quite as
um you know it's not quite as dark as some of the other darker areas and you
want to see if you can tease out data Milky Way and make it look you know just
a bit bring out just a bit more than what might be visible so what I'm going
to do is see what happens those are 10c
images and you see the trees got fuzzy this was a 242 second image so there's
data trapped in here that I plan on pulling out teasing out and seeing what
I can get and stacking all of these images together along
with that um 4minute stack and seeing what I can get um trying to get a
natural image is difficult but can be
done um combining a few different techniques because we want the ultimate
goal is we we essentially want to se to look something like this we want it to
look the way it did before it let's take the highlights out out
briefly and you know so it's not so clipped and we we're going to want the scene to look
we can do all this in postprocessing and the way the trees look here the sky is a little bright
we're going to modify that when we process so that it looks more of the way
that I remember it and uh so as usual I've shown pictures I go
after difficult times where there's different there's different lighting going on with the
moon um and the sky and try and combine those because
the cosmos isn't just about when you do Milky Way Photography this is what you think of
for Milky Way season but the cosmos is here fulltime and if we only focus on
one part of the Milky Way we miss the opportunity in IM of Imaging something
turning around this is when that other when the galactic center is out turn your cameras around and do a do a shot
of this side of the Milky Way heart and soul double cluster and dram NGC 761
m33 these are some other um there's other clusters that I
can't name because I haven't done my homework yet and if you've listened to Global Star Party you know that I point
things out regions that I swear I'd do my homework and then still haven't most
of the time when you get a streak like this it's it's usually a plane but in
some cases it could be a streaking meteor but
um but yeah there's more it's Beau you know our own view of the cosmos and when
we try and capture it um it's kind of a kind of a metaphor for um
you know how big it really is there's there's a lot more to it the Orion side
the signis side um especially in Winter if it does
clear up you know that's that's where you come down here and you experiment
with and comets are in the sky try and catch those you go for this region and try and capture it so
between doing images of just certain parts wide angle images of different
regions of the cosmos to different deep space objects and then back to the entire wide
field it's uh there's never a never a dull moment even if all you do is just
look up and look at the stars and there's always something to work on that again this is why I say trees are
something I want to get better at because in what is otherwise the nice
just test shot over a Snowy Road my trees didn't come out so we just have to
uh continue the work on that and so so with that Scott I will go ahead and give
it back to you because I'm sure I've about run 15 minutes and I know we want
to get pra on but uh as always we tell everyone who's
involved with astronomy without reach we always say keep looking up and that's
for a reason because we the sky never disappoints no matter what's going on in
your country in your your uh World um
you know and whether the media tells you that there's a planetary parade um the
planets are typically out during uh this is winter going in the spring the
planets are usually out there between spring summer once it
gets to Summer they it depends depending on alignment they begin to disappear but
stay up long enough you'll see at least one or two of them so sure sure there's
a question uh from Dean bador uh watching on YouTube uh he wants to know
where you're going to be or if you're you're going to try to be uh somewhere for the
eclipse for lunar eclipse I am going to try be somewhere I haven't nailed it down and I
need to nail it down soon I was out at uh Alcona um that last one in November um
22 or 2022 and I want to try to go to a different site for uh this one in
24 um and try and capture it similarly to what I did in 22 so not yet I think
we're going to look at the cloud cover because we've had a lot of cloud cover here in
Michigan yeah for sure and that as we have here yeah it's hard to look at the
cosmos when it's cloudy you just have to you have to wait use your tools those of
you who might be interested spotwx
docomo for looking at your region all over the globe and looking at um
predictions of cloud cover precipitation it's it's uh weather stations are out
there astrospheres some of the same
forecasting models there's The Weather Channel which I think is worldwide there's Weather
Underground and then I think there's even more sources than just those four I named um when the sources tend to line
up and say that it'll be clear that's usually the best time to believe that
it'll be clear um when I went out those few images I showed where I was just
trying to get um an image of Orion I went out there it said it would be clear
for a time and I stayed too long because
um I uh I got there and then the cloud showed up after I got a few images got
just enough for the stacking and then the clouds came and just shut the whole Sky
down and the Cosmos the show was over it it felt like they closed the
planetary you know I used a proverbial they but we know you know know the night guy that not always do things work out
for us you know they don't work out all the time but we uh we make lemonade out
of Cloudy Skies exactly that's what we do how we do that's right so um uh we
have a few minutes before uh pranvera comes on uh so I am going to play um
another wonderful video this is from NASA and it's uh has to do with echo in
the Big Bang so thank you very much Adrian thank you for having me Scott and
thank you deid for always uh having me as well and uh hopefully you enjoyed a
couple of the images that I shared today that's my pleasure great excent okay
let's um let's see what NASA has to offer us here
[Music]
[Music]
for [Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Applause] [Music]
[Music]
[Applause] [Music]
[Music]
la
[Music]
[Applause]
[Music]
[Applause] [Music] [Applause] [Music] [Applause]
[Music]
[Applause]
[Music]
for
[Music]
[Applause] [Music]
[Applause]
[Music] [Applause] [Music] [Applause]
[Music]
[Applause] [Music]
[Applause]
let me get my sound back on that was incredible uh I'm going to have to watch that all over again I loved how it
started with the pale blue dot and then just took us all through the universe
and uh showed us uh you know all these super structures and everything it was
incredible anyways I hope you enjoyed it too um our next speaker is none other
than P Vera heini PR Vera is just back from Mona where she was doing asteroid
research um and she's here to tell us all about it bran Vera thanks for coming
on to the global party it's my pleasure thank you for having me Scott um I'm sorry like today
I've been having computer issues I don't know what's happening but in case I disconnect I will be right back from my
phone or my computer so I'm having it side we all happy to see you thank you
yeah thank you and it's I'm happy to see everybody here uh I see David AER and
Levy and Oscar Caesar and a lot of other folks I love being back in this show and
I haven't been back in a while uh usually my schedule is really crazy trying to uh you know deal with grad
school and then whatever free time I have I try to uh either travel or do
some Outreach or all of that but uh this was definitely an experience I've had
that I thought it was worth coming here and talking about because I've been to
so many places around the world to so many Star parties but what I experienced
at Mount AA was was completely different this was really special so I have a
series of photos that maybe whoever follows me have already seen them on my
socials but I will just uh share my screen here and just go through some of the pictures um so I am a thirdy year
PhD student at QC Santa Cruz and uh my research focuses in understanding the
composition of hydrated asteroids so hydrated asteroids are a
type c of asteroids so in other words uh long time ago they had a lot of water
and ice in them and they formed beyond the snow line so they form Beyond like
at like Jupiter or where trans neptunians are but because of the uh Gas
Giants and the migration of the gas giants Jupiter and Saturn pattern they
actually moved inwards so these hydrated asteroids had also early in the solar
system enough uh aluminum um radioisotopes that actually
generated heat and they were able to melt the ice in the interior therefore
they started having liquid water running in the interior of these planetesimals
and once you have liquid water running then you will definitely have a change in composition because water will
therefore go ahead and form secondary minerals like phyo silicates and
carbonates and uh other minerals that when we see these in the surface of of
the asteroids through spectroscopy we can literally tell or piece together a
piece of history about what that particular asteroid has gone through so
this is a method that we use and spectroscopy can be in many wavel but generally um a lot of it it's taking
place in the visible range so the light that we can actually see but the work that I do I actually focus in the
infrared mid infrared around 3 Micron because that's the best window for us to
be able to pick up hydration features and Organics and all of that because
keep in mind that if we have liquid water running around in these planetesimals they also
there were there should be Organics so any soluble Organics that dissolved in
water and then water was floating around was redistributed around these
planetesimals and then it probably even came close to the surface or even exhaled the planetesimal with plumes and
all that so everything was deposed in the surface so when we look at these in
the infrared we can see all types of salts and Organics and hyd ated minerals
and it's really interesting because some of these objects are in the same damn family like they have the parent Budd
and then an impact happened and it scattered all these pieces and then we have family members like siblings and we
would expect the siblings to be the same right but that's not always the case we
see differences between the family members and the parent buddy and it's
really interesting when you get to the roots of it to try to make sense of what exactly happened here so that's what my
research is focused on and the coolest thing about this whole thing is that
it's almost like walking in a frozen lab in time like you can you get to go there
I mean we don't really go there but spectroscopy allows us to understand the composition of these objects from the
comfort of being here at Earth through the reflected light from these asteroids
and different minerals in the surface of these asteroids they absorb light or
they reflect light so we can read the absorption bands kind of like
fingerprints and we can determine exactly what they're composed of so a
lot of my work that I do as part of my thesis is using some of the telescopes
that are located in M AA in more particular I use NASA's infrared telescope facility which is a 3 and a
half meter telescope and uh to be able to use this telescope you first off have
to submit a proposal with a motivation and a goal and a a project that they
might find worthy it's not as competitive as applying for James web telescope time but it's definitely
competitive and I was lucky to have two proposals accepted one last year and one
this year and usually when they accept you they will give you several nights over the course of half of a year it can
be one month one night of a month or two nights in sequence and every time I used
the telescope in the past I use this remotely from my office here because
they have this setup such that uh the telescope operator is on site uh they
slew the telescope and all of that but then I get to collect the data and I can do it from here from home but since they
gave me two back toback nights this month I was like you know what I'm just
going to go there in person because I needed to experience this I needed to visit the observatories to be at Mount
AA and experience what it's like using a telescope for research purposes I have
been to I would say most of the large observatories across the United States
but all of those visits have been just me walking around taking pictures having a quick visit this has been different
because in this I am like working with the equipment I'm using the telescope
for something that I'm aiming to find to answer questions that we have about the
formation of the solar system so this is one of my favorite photos because behind
me you can see a number of Domes there are 13 observatories and they're located at 13,000 ft so to go there you actually
have to go at the base and this was a NASA funded trip a along with University
of California so I had a room there at the base that's where I went to stay two
nights prior to starting my observations because they want you to get acclimated
because of the altitude some people uh face symptoms and so I stayed there for
two nights and then uh when you go up to the summit there is a limit of 14 hours
you cannot really stay there more than 14 hours and at times I was like I want
to go there during the day and take pictures and videos and then I had observing all night but that would put
me over 14 hours and they don't like that it's a rule so I was trying to
combine my photography and filming and observing all of that going back and
forth and I was lucky they gave me a four-wheel car because that's only what's allowed to go up there so I had
the flexibility to go back and forth between the base and the summit at my preference
um the one Dome that you see here all the way to the left of me it's the NASA
infrared telescope that's that's my office where I actually worked there it
was really nice uh behind me it's uh two c telescopes each of these domes has a
10 met telescope inside I did not get to go inside the other domes unfortunately
I wish I could but uh there is every time there are some telescope operators
there and also an assistant uh they also have this rule where not only one person
gets to be at the telescope because of the altitude they are worried that some something could happen an emergency so
they always have to be two people on site plus The Observers during the day you would see a lot of tourists going up
there watching the sunset taking photos but then once the sun is set the security will tell all the visitors to
go down and it's quiet and it's really dark uh this is also another view so I
was standing at NASA's irtf telescope looking down and you can see both cek
telescopes and then all the way to the left is also the Subaru also another 10 meter telescopes uh so here behind me is
the Subaru Subaru has a different type of Dome construction it's not like kek
or NASA irf it has this Dome that splits in half and uh moves um so
it it is interesting cuz all of these observatories I've heard of I've seen many pictures but it's different going
there and visiting in person uh this is another closeup look of the nasas irtf
facility you can see the parking lot is empty because there is usually nobody there sometimes the telescope is used
during the day because this is operating in infrared so there are people looking at Venus or Jupiter or something so they
definitely use this during the day um so I got to actually go inside during the
day and take pictures when somebody else was using the telescope uh this is just
a picture uh and of course I brought my flag cuz I'm from Kosovo and I was so proud to be there it was actually
kosova's Independence Day at this day when I was there waving my flag and you
can perhaps the photo doesn't really do justice but you can tell how magnificent
this equipment is it's enormous so that's the telescope the orange part and
then everything underneath that you see are all the tools all the equipment different detectors because this is
operating in infrared we don't have just one detector we have many detectors that
cover different wavelength ranges and I believe um so this is just another goofy
selfie of me because I was so excited to be there but yeah that's behind me the blue one is actually the detector that I
use it's called spec and it covers from 1 point something to four five Micron so
that's the area of uh the infrared that I'm interested in around 2.9 3.1 3.2
that's where we can detect a lot of hydration features um the ammonium ions
and vibrations that are occurring in the ammonium salts and then the Organics the
carbon hydrogen band everything is happening in that wavelength and it's really nice that we have this detector
and it has a moderate resolution but it does the job like I can literally look at the asteroids in space I choose the
targets and then I get the data and then afterwards I process it when I get back
home that's just another view of the spec detector and behind me you can actually see two other women that's the
telescope operator it was the daytime and the assistant so they have to switch between between the detectors so this
was my detector so they had to remove this and put another infrared detector
for somebody else who was observing Venus during the day so they always have to go with tools and I was impressed
with these badass women doing that job it was really really nice and I just was
there witnessing all this and then this is me I it was cold I got to mention
during the day it wasn't probably that cold with a light jacket I mean there was snow around and for somebody to say
that oh yeah this is a picture in Hawaii and that's snow it's quite quite crazy
because people are not generally associating snow with Hawaii and when I was flying there I had my winter coat
and all my winter gear with me people were looking at me weird on the air airplane they were like where the hell
are you headed to but that's me at night when my when the telescope was running
Imaging my target taret usually I would land it I would let it run for a couple
of Cycles which would be like half an hour at a time and then I would just go
inside the Dome there is no problem you can go inside the Dome the telescope has some lights too so because we're
operating in the infrared light doesn't really uh bother much so I just wanted
to go there take some pictures and these are just some of the shots I took of the telescope so the sled the Dome is open
you can see the the sky through the sled uh the telescope is just I love it it
just it was this nice equipment that I get to operate I get to use and it's my
data and it's looking at the targets that I picked and I was so happy and so excited about this this is just another
angle so the telescope is sing it's an equatorial Mound so there is no need to change the plane when it reaches the
Zenith and uh also this is one of my favorite pictures because on top there you can basically
spot Orion and it looks like this is straight out of a sci-fi movie it just I
love all the colors and the sky and the telescope how everything came in together I really like this image very
much um and then I believe this is just a time lapse that I let my camera run
why while the telescope was collecting data from the targets I'm surprised it's
working in this computer cuz I could not open it earlier and then when I was there I had enough time all night long I
had like two full nights to just observe asteroids and mind you when I look at
these targets I don't only look at the asteroids itself I also have to look at
several stars that are near the in the area of the sky where the targets are
where the asteroids are and these stars have to be uh similar to our sun because
because we have to use their Spectra to subtract the asteroid Spectra from them
so this way we have this technique to uh correct for the air mass for the
atmosphere for isolating the reflected um Spectra of the asteroids all of that
but I had plenty of time to play with my camera so I was just going there by myself setting up my camera and putting
my phone taking all these pictures it was fun I enjoyed being there this is
just a picture from the outside of the Dome it's pretty big it's good that we
have some cars there so you can kind of have a reference of the size and then
this is just another night shot uh you can it was the moon so I had the moon in
the sky but Moon did not come until later maybe 10:00 or 11 at night so I
still got to experience dark dark skies but then once the moon came up it was great because it was nice to do some
photography like this having the domes lit by the moon and and then yet you can still see the Milky Way and I am not an
astrophotographer but you could probably pull out a lot more from this picture I'm sure and then again me just
wandering around with a car I had the vehicle I would just stop set up my camera freeze for 13 seconds bam like I
loved doing this so much and then one of the coolest things one of the coolest
things and Scott if I'm running like out of time please remind me cuz I lose track of
time you are good don't worry perfect so one of the coolest thing I experienced
was seeing zodiacal light I have seen this before at Star parties not as
strong as here but it was so bright to the point where it almost was like light
pollution coming from a city that's how bright it was and then Venus was right
there for the first time in my life I have seen my own shadow from Venus if I
was putting one hand and doing with my other hand on top of it I could
basically see the Shadow and there was no moon no other lights around it was
very very impressive this is just another picture before the moon came up um I loved that
the Orion was there but it was very high in the sky and I had to wait until it went all the way down uh but by that
time Moon would come up so and then this is I forget if it's I think it's Sunset
yeah it is sunset but from up there at 13,000 ft I saw some of the most
beautiful sunsets and sunrises because I was going Before Sunset and I was coming
down when the sunrise was happening so I got to witness both and again this is from the same spot from the parking lot
of NASA's irtf and that's C telescopes and also one cool thing despite that
there are no large cities around with light pollution even if there was the clouds cover everything and that blocks
any light from coming up uh but I just love these images because
these are going to be my memories of some of the times I really had a great time I walked up to the other side of
the domes where you saw on the previous pictures behind me and then looking down
so there all the way to the right is NASA's irtf that's the parking lot where I would usually take all the pictures
from and then it was sunset lots of people were behind me taking pictures
time lapses of the sunset it's beautiful and then this is just another picture
there are so many photos that I just had didn't have the time because I have so much work to do with my school I haven't
posted everything but I will keep posting eventually these are I believe just done from my phone so the
resolution is really not good but I love how the domes look uh through the sunset
all these colorful lights and then just one more and then I
just love looking at my office that's where I got to work for two nights and
be there for four days it was it was really nice very exciting this is also
another daytime picture of the domes behind me when I went up there uh waiting for the sunset so these domes by
the way look really tiny in some of the pictures but once you drive there and look up these are enormous domes all
these telescopes are big like 10 met 4 m 3 m like they are
gigantic um this is just a picture of me and then this is another one I believe
this is a sunrise that I took from the base not from 13,000 ft the base was at 9 9,000 ft I just loved how the clouds
were right there this layer of clouds very detailed the sun was coming up the
colors it was very peaceful very beautiful this is just an iPhone shot of
the Venus and zodiacal light like getting the zodiacal light with an iPhone is just crazy to me
and then these are just some other photos oh by the way these are just some of the pictures from the control room so
there was two control rooms in the same room but one set is for the telescope
operator where he Lo the telescope he tells the Dome to open to rotate this
way that way I don't do that my job is to control the settings when I get my
observations I set what exposures I pick the targets I choose how many cycles do
I want to run how many coads all of that and then I also control the guide dog so
it's kind of like a guide telescope when you do aop photography a lot of you here do that when you have a autoguider to
keep your object very precisely in the field of you that's exactly what we have here
also and then that's I think from the first or second night me just collecting
a lot of data that's the telescope operator's uh desk I just took a selfie
there and then uh in Hawaii it was beautiful I got I think two extra days
to sightsee the island the Big Island I've never been to Hawaii before so I was freezing up there and then 45
minutes I drove down and it was ready to go to the beach I didn't go in the sea
but you could swim it was 27° C and I saw some of the most beautiful sunsets
again this is just a photo when I was driving in a highway like this is insane
um I guess this is just another picture I took and then one of the coolest features that I liked about Hawaii was
visiting some of the Volcano National Parks and uh volcano like lava fields
and features all the bazal Rocks because I study Earth and planetary science so
my studies are not really concentrated just planetary I also am curious about the geology of our own Planet so I took
a lot of photos and it was just nice I've never seen lava Fields this much
detailed and uh I was ready to leave I went by the volcano during the day it
was my last day it was just steam I did not get to see anything but then it was
midnight and my flight was leaving at 6:00 in the morning I swear I was in my
pajamas about to go to bed somebody texted me and said the volcano is erupting and that was about an hour
drive from where I was staying and I just hopped on the car and I was like I'm going and it was incredible like
this is the first time I've seen a volcano and it happened just before I took off and what I liked mostly about
this was that I could see earth like this was the heart of the earth reshaping itself in front of my eyes and
then despite all the bright light you could see the sky the stars around it
was very surreal like this one photo I just really really like on one side it
was a volc and then the other side a clear sky and I like how they put these tiny lights in the national park they
kind of look like lava things and then this are just some close-up shots of the
volcano itself uh I I really did not expect to end the trip this epically it
was really really nice this is a picture of the lava it kind of looks like a city when you look from the airplane when
you're flying at night and then this is one of my favorite pictures um it's like
a volcano and then the Stars the sky and then the moon on the left it's all this
combination of the universe and planet Earth and the stars and all these colorful lights I it's an experience I
wish a lot of people get to have because it's it changes you it's very very
special and uh this is I just wanted to end it with this video somebody let me
borrow a lens some photographer random people were driving there at 1:00 in the morning
and this was a very powerful lens so I got to zoom in I think I was a mile and a half away from the volcano but for
Christ's sake this is crazy and I was so happy to be able to end the trip all the
nights were perfect weather I got all my data and now I am back home I am uh
processing that data and next month I actually have my qualifying exam for my
PhD where I Advance into a candidate so I'm a little bit nervous but I got lots
of work to do and I'm so happy I came here to share all of this I hope I did not take too much time I lost track of
time but thank you so much Scott thank you so much pra it was
fabulous thank you David let me bring you on David here we go yeah yeah I mean can
you imagine you're going to Mona okay and those of us who have been know how
amazing that is and then to see a active volcano on the same trip I my goodness
that is just unbelievable at the NASA irf they had a screen two screens one
was like a live view of the Dome so I could see the does rotating and the sky and all that and then the other one was
the volcano so the entire time the volcano was just steaming and I heard words them saying it might erupt in the
following days and the following days and I was like why is it not happening while I'm here because I'm off and then
it just happened and I would like to thank my friend tunch from Turkey cuz he messaged me on Instagram at midnight and
was like the volcano is erupting go see it because I would have probably gone to bed and left in the morning and I would
have been so mad to have missed it oh yeah so some people would would have
said you've manifested that Carl Jung the um would have said he didn't believe
in coincidence he believed in synchronicity so so yeah so something
happened there but I have been to so many trips Scott and I have enjoyed them but this one I felt it to my core it it
really was very it did something to my heart and I very much enjoy it and I
know that I'm going back uh the first chance I get right well for all of you
guys out there watching this I mean you got to go and follow your dreams you got to make them happen you know uh no one's
going to make them happen for you but uh you know take those opportunities uh get
involved if you love astronomy get involved as deeply as you can so anyhow
uh thank you so much pleasure and it's nice to see everybody here hey Robert
Reeves I'm glad to see you here very
good let me get my microphone down good to see you too okay all right all right so our next
speaker is Cesar brolo down in uh Argentina and uh Cesar um let me find
you you're hiding here amongst these people there you are it looks like you
have a beautiful sunset behind you with a comet uh you're muted
or your microphone's not [Music] connected now now okay that's good now
okay okay yes I I I I I yes yes I I
touch something yes I'm older with the technology and you know that um yes so
you're you're going to be talking about the star party VI Grande is that correct
yes yes uh in Buenos cidus we we use more the instead the L um we
call it bash Grand but it's something yes outside
vosis for example in Cordova or in mendosa the province where we made the
they use more B grande grand okay but in Bueno or in
some places or like Patagonia we use uh most the middle bash bash Grand totally
argen cool I like that pronunciation but B is is is correct totally but we use
more our style of of pronunciation um yes my father from the
north of Argentina say poo and I say poo like a chicken and we all time we change
in Bueno or in part of Argentina the pronunciation uh L
L to a uh well we are a
few a few weeks of uh of um our annual
start party in L Moses um in province of Mendoza let me show you where is with uh
Maps applications um
here you can see this is uh actually we
are using two different hotels and uh the first one
is the the hotel termas laeno is where is this is the field
where we use for put the telescopes is a is an
area it's totally dark this road in the night anybody goes uh in this area and
the another hotel that we use is this we are we have actually complete this and
we are filling with people this hotel wum this year we are
using I think that we are feeling the totally the the both
hotels um the road from from
buenosaires let me show you where is this is near to the something that the
mountains that we call it the pre Corda the losandes is not smaller than Corda
especially but the name of precord is the the the part of the were
pre is like something because it's older than the Corda de losandes that the the
mountain that you know that that is between Chile and
Argentina this is for for give you an idea this is lo
Moses where we are making our store party this is the Corda de losandes this
is the precord and this is Chile and this is the Pacific Oceans
the altitude is around 1,500
M you can see how from
from from this area you are going
up to here here how high is it
Cesar 1,00 here is around 1, 500 00
M um it's not more I I think that is is
um a little more but uh 1,700 M no no more I think it's not to
2,000 M because 2,000 M isn't the Kei Resort in Las Lenas in in in this area
you can see how the precord grow this part ah yes and now
yes you have more vales and this part is is
CA here you have over 3,000 or
4,000 4,000 Ms yes this is complete
snow paks yes this is amazing I show you some
part of this in this area this is the the
Lenas Lenas ski resort this is the
road I went sometimes to to ski in laen it's amazing in winter but of course
that we don't need snow time now and the we are making this in the end of summer
because in Autumn you can get snow and you are in problems if you
uh have snow bad weather for us it's beautiful but no for astronomy
you know and um well I can show
you there the for example the the old place where we make the bash Grande is
the Vash Grande star party is the name because the the our first St Paris was
in this area where is the
the the area of Vash sorry this is mendosa this
is I completely lost no here this is the original place for for
the star party in the area of San Rafael and in this area we make the first star
party but actually we move to l es here is more in middle of
the mountains you can see the the difference between this area that is high but it's around 700 M and here do
you have 1,500 M um a little more um
more dark sky much better for for observations and I show you the road if
you like to go driving for wois do have
uh 1,250
kilom wow here is vosis yes you you can take a fly of two
hours from buenosaires to San Rafael every day do you have do you have
one or two flies or H take the adventure to go to their Argent roads I say
Adventure because our roads are a little not so good like in America in United States but um actually the
188 is a empty Road in the day where you
can grow some truck or another cars but you are ER you can drive lonely in in
this uh in this road I show you
indications for [Applause] example my one of our office
here here and you have if you go to from you
start from wos for example you need uh one day and
another day one and half day to go normally we we go to San Raphael we
sleep in San Raphael and another day we have a 200 kilometers only that is like
uh 3 hours driving no more but you need more time
sorry because of of obviously you need you need um driving
it's it's a long trip like allum in in Argentina I can I I draw in
United States uh for example from kilargo to Atlanta and maybe is like kilargo to
Atlanta maybe it's a little it's a little shorter it's like a woid to this
area uh this is like a go to um kilargo
to for example maybe North Caroline I for
example to to have to go to to give an idea Scott um and well I I'll show you a
presentation I'll change my my
screen maybe you can see that you can see the change of of the screen
now um no I need to stop share and share
again here
okay can you see the presentation now okay um well this is
the St party Los Moses this this year it will
be um 27 28 29 and 30 of
March here is the phone of Cecilia laki but in the end of presentation I show
you again the numbers and my email if somebody can contact us because we have
a place actually and the people can contact to Cecilia or me to
to to inscribe to have a a place in in
Star Party Los mes this this year the price is excellent uh is with all
accommodation with Foods um really it's a it's a a good opportunity for the
people from United States from all South America uh or another countries
uh if you like to to have a um to know a great place and a beautiful uh Southern
Sky uh that looks um totally amazing uh
at niked eyes and really um it's a it's a great opportunity to to enjoy with us
the the southern Skies well here is the same that I showed you and now you have
the time for example 13 hour 45 minutes um of course that we don't we don't uh
recommend make this all in one day because maybe you can go into make this
part in night and it's totally not recommended M driving you know the the
the the you have a lot of cures um in the end of the day it's not dangerous
because it's not a you know a fall or um because it's a good road but it's
for for driving the day of course that don't don't make any dangerous because
in the night you have your advantage are totally low driving um um one day for go
to for going to San Rafael and another day only two hours half three hours
going to Los Moses going to the mountain here do you have the values
actually for Las Lenas and this is the the value in in winter in Winter because
Las Lenas in the night ER they turn on
turn on the lights for skiing in the night you know but Las Lenas in this
time of the year never turn or turn on
the illumination is totally this value is is
unreal outside the time of skying because they turn on the lights
only two or three hours in the first hours of the night in winter only not
now in Argentina um to use the the ski resort
and use it for the people skying you know in the night um but the the levels
are much better that two um the quality is really of the sky
is amazing it's very easy to make a great great photographies because the
the and The Sensation to see the sky is amazing too this is the the
hotel laeno the first hotel this is the landscape from the
hotel wow is yeah nice part part of the people I I'll
show you uh to the audience um the
picture from the hour last start part in 24 2024 and for given idea because it
will be H at the same place people enjoying and
me um well I'll show I I I I need to say that
I show in in in these pictures in
in in March in May in May of uh
2024 um it's amazing to return to see again and feel the idea to return it's
you know that that you you feel great when you see the picture and say okay okay in four weeks I'm going again to
this place um actually I'm my father of uh
80 80 86 years old 86 years old told me
sesar I can get I can go with the S party can you no I he said me I can go
with you to the Sur party yes of course my father many many times and yes is
very enthusiastic um watching of of the sky
and you know that is a is a great he have these great ideas about things uh
he held me a lot of time when we made together uh domes or parts of telescope
mechanic parts and he's a enthusiastic
uh um amate astronomer um in in his uh autumn autumn
uh years of life and you know this is
all about the people connecting telescopes all that in the entire War
you can see an a star party and you can feel like in your home because you you
know that you can change the country the place but you when you see people I'm a
stronger with telescope you feel like you are ever ever you are in home I feel
the same I remember atana Georgia um for me I remember I remember
the the talking with the people like in my own in my own language because for me
I've felt like uh this people like my friends um this is the same this is
totally the same same um in Argentina we uh like uh comparing the the price
outside outside um you know uh we don't use tents H to go to the star parties
because the hotels have an excellent price um outside the the season outside
the season um uh some people say okay do you have I need to go with t to to to to
to with a camper and we can use uh totally this beautiful hotels at price
at price that are really a gift because when when I say to the people oh the
price is this for me I am totally outside of the business of the hotel because our idea is only we a sponsor
and work in the store party I never I never see the the things because the
people pay directly to the hotel at the price that that was totally H ER made
for visitors and a special gift prize really for this out of season prices
that are impossible in season this hotel have maybe three or four times the this
price in snow or skiing season and this is why we are go into this uh and it's
very good for for these hotels still working outside the season
one of first to to don't be uh the shiny like a
movie and and another thing that because all the entire year is full of people
and they love to to receive people the entire the entire year um the price
of outside the the the season for us is really a
gift and this is where is is the the people h i I love the people sharing and
so proud of his years his works this is Alejandra velli the many of them uh are
people that uh are actually we are friends um we share a lot of things so
so different so specials and really really um it's a pleasure for for us
make every year this s party
paoo made a lot of gear from from explor scientific Scott because one of the for
example the yes the successful of of the yeah but the successful of this that
that for people that take a plane they a fly maybe they for example Juan Pablo
have an excellent an excellent C in his home in his Observatory but for to go to
a party ER in a fly is a lot of is complicated to to carry an Schmid ceran
telescope um he love for example use their their own 80 mm
APO explor scientific well but many people say okay no problem
but people that came driving they they carry the all
equipment wow look that yes this is only around the corner only 14
kilometers this is the ski resort Las Lenas in s in summer this is full of of
of um for example this line I is is so easy line for for skiing that I could I
could Skip it's very slow very flat yeah but
it's totally white of course in in summer and and in Winter sorry this is
in summer in March wonderful wonderful yes yes yes around around thank you it's
a pleasure it's a pleasure sharing this with us um yeah uh where can people
learn more about this um star party let me show you now there are
pictures from the from the Star Party sure and now fastly I'll I'll give you
the contacts oh yeah I was really
yeah we use more WhatsApp this is the the the number of Cecilia laki Cecilia
is is returning from United States today um she's in contact with us because
she's um she's G taking the all all um request of of people that
like to to to participate of our St
party wonderful so they just get the WhatsApp um yes yes and me email because
cesar.com and my yes and yeah yes yes and my my my cell phone too yes
wonderful is is my what WhatsApp too thank you very much to the audience
thank you so much oh it's a pleasure what a pleasure thank you very much good
night okay all right so um uh let's um bring us over here and uh
um we will bring on Robert Reeves Robert uh thank
you so much for uh gracing us once again with uh your knowledge of the Moon and
um uh we are uh you know it's it's it's been we're
now at 167 Global star parties I think you've been on maybe 50 or 60 of them so
far been a couple and U it's been a couple I have to think twice what have I spoken about before so I don't repeat
myself we can always hear it again I mean it's it's okay it may happen by accident but um yeah a lot of lot of fun
things have been happening recently and U as you'll see in the first couple of slides um you know about a year ago I
was talking about how I inherited a lot of the original lunar orbiter photographs that were at the Johnson Spa
well the man spacecraft Center back then now they call it the Johnson well yesterday I took delivery of all of the
rest of them they're they're they're behind me let's see if I can oh my gosh uh that
stack yeah uh that's 500 pounds of lunar orbiter
photographs I've got a I've got a catalog them probably if you put them in to end they would stretch from here to
the Moon oh well maybe from here from here to Houston maybe yeah I've got my hands full getting them sorted out and
cataloged and everything and calling out the duplicates and so forth but uh it's
going to be a fun trip because um the moon has been my companion um well
actually um you just just several months after Explorer one the first American
Earth satellite that August U the Air Force said the heck with this Earth satellite stuff we're going to the moon
and they launched the first of the pioneer uh space probes uh headed for
the Moon unfortunately it ended up in the same familiar Fireball that many early space launches did but um just in
August of 1958 we were heading to the moon and that caught my attention that among several other things um you know
ignited this you know literally lifelong passion I have for the moon so um um it
continues on and I'm I'm so so delighted to be the keeper of this Archive of
history from the Luna Orbiter project but um anyway um you another thing that
um related more to what I'm going to be talking about tonight uh another thing that I got back in 1958 at Christmas
time I was given the book 10,1 questions about astronomy uh James pickering's uh
version of it 1958 I remember question number 117 what is the largest crater on the
moon well at the time the answer was clavus nowadays we know that's not quite
true and that's what I'll be talking about tonight uh uh Echoes from the cosmos well clavus has been around since
the beginning of the moon it's one of the older creators on the moon so for as long as the solar system has been around
uh clavus has been here for most of it so let's let's take a look at one
feature on the moon and uh let me go to screen share and see if I can get
everything to work and uh you are sharing screen yes uh okay there's my
typical title slide postcards from the Moon and uh I hope you're enjoying the ones that I put up on Facebook uh not
necessarily daily anymore because of other things but as often as I can so um
like I said I I I inherited all the rest of the lunar orbit pictures and uh Rusty
the the the she's got a reputation of guarding my my Moon pictures uh she'll
sit on them and make sure Nobody messes with them but uh yeah um I've got a
fairly small office so this going to be a challenge sorting all of these out but uh in the meantime um if I push the
right button we're going to talk about clavus Crater uh the the largest visible
crater on the moon um about 225 km across there are larger craters on the
moon on the back side of course and we have since found that several other craters on the near side are larger but
back in 1958 uh when uh we didn't have satellites in orbit around the Moon we
didn't have these lunar orbit pictures to measure precisely U with with
geodetic measurements like we do on the earth um well back then we thought
clavus was the biggest well since then we we found out clavus is actually the third largest on on the near side of the
moon but um as I discussed a little bit further we'll find out that uh the
definition of a crater U clavus and these other two features that are larger
than it U the definition of a crater definition of a basin has become very fluid lately so um glavius may not be
the third largest crater on the moon at all uh it could be something else so
let's U press on and uh see what kind of Mischief we can get into now as Sunrise
Shadows approach just past the first quarter moon U down at the bottom we see
Moretta crater um a lot of people mistake it for Tao very similar in appearance to
Tao but Tao is actually north of clavus and uh just nipping into the top edge of
the field of view still filled with Shadow much like clavus the big dark gouge in this right in the middle clavus
is still completely shadowed only its eastern Rim showing uh in in the
sunlight but a couple of hours later well now the sunrise has crept a little
bit further it's spilling across the Eastern rim of of clavius and the first
rays of Sunrise are now striking the opposite Rim but there's also satellite
craters inside cavus they're fairly large but clavus is so big they these
look small but these satellite particularly clavus C and D um catch the
first rays of sunlight just skimming across uh uh the walls and illuminates
their rims but the floor of the crater is still in Shadow so this creates an
effect that we call the eyes of clavius and clavius itself of course named after
uh Kristoff CLA um a German mathematician 15th century German ma mathematician and U Giovani rioli who
named U you many of the large features on the moon and those names still stick
today uh 350 years after he did it uh he must have had held Kristoff CLA in very
high esteem because he named the largest visible crater on the uh on the visible face of the Moon after this this
gentleman and um moving on a little bit now the sunrise is complete uh we're
seeing the floor of clavus illuminated and this transition from just being a
shadowy gouge along the Terminator to completely illuminated crater can occur
just in the space of an evening so shows the Moon is a fairly Dynamic body as far
as your your visual observing because the shadow along the Terminator it it it
U changes almost hour by hour of course now we can see Tao up above and uh down
below uh to the lower right we see morus and see how similar they are how people
can easily mistake them for each other a wide view and U we see that U
you know pavus is a fairly substantial crater get my cursor going here we see
it circling clavus here but uh across the face of the Moon there's a lot of
other traffic around here that catches our attention the Rays of Tao coming down uh moretus over here uh the Curious
oblong craters uh over here and Shard U also very large but down along the
bottom Terminator notice this big monster down here this is Bailey 301
kilom in diameter um 60 OD 65 kilometers larger than clavius but the back at the
beginning of the space age uh we didn't realize how big Bailey was so uh once uh
figured out how big Bailey was well it was now the largest creater on the moon but wait a minute as we understood the
the geology of the Moon better um it was determined or decreed that any crater
larger than 300 km in diameter was no longer a crater it was now A Basin so
good now cavus is now the largest crater again because the one bigger than it is
not classified as a crater but as a basin so Bailey was named at the same
time as uh clavus almost 350 years ago and uh uh we
still call it a crater by U uh just the U the tradition the inertia of it being
on the map as a crater all this time but uh in reality Bailey is a basin we we
kind of give it a dual designation and moving on
uh here we see the territory immediately around clavus and uh one thing that uh
strikes this is you know clavus is pretty darn big here but it's got some large neighbors as well Longo Montanas
here and U maginus and then up above Tao of course but uh one thing that you see
is common between uh Longo Banos Magus and cavus they all look very very worn
these are old old craters almost 4 billion years old formed just very
shortly after the formation of the Moon and uh Tao is the interloper very fresh
very new got crisp rims Rim around it hasn't been worn down by uh billions of
years of space weathering and and additional impacts so here's uh Tao uh
almost 40 times younger than these other craters that uh have been there for
billions of years and another uh view I verbally jumped
ahead of myself uh discussing Bailey but U another view of Bailey Basin now 301
kilm in diameter so it upstaged U glavius for a little while
but now that it's a basin yeah we can go back to be calling clavus a Bas I a
crater now too maybe we'll see that could be very fluid as well so
continuing on here we see little more territory to the north now we've got uh
here whoops I didn't mean to do that let me back up here is clavius again circling
circling the wagons here Tao and then up here this massive ringed Basin plane
here uh desri crater uh we didn't even recognize desandre as being a creater
until the 20th century before then it was simply called hell plain uh named
after the creater hell right here named after father maximilan hell well-known
astronomer from the 18th century but uh did our measurements and U surprise
desas is bigger than clavius so cleus got kicked down again
there landre is the bigest crater on the near Side of the Moon um CL clavus is
now the second largest but we have uh different ways of analyzing the moon now
not only photographically where we could measure it and the uh or the the the
diameters of craters but the gravitational pull of the moon's surface
varies and we find that over a basin there is an increase in gravity at
center of the Basin and a decrease in gravity at the edge of the Basin now
this isn't enough that an astronaut be able to jump 10 feet higher on the moon but it is it is detectable uh
differences in gravity and these indicate there is a very basic morphological difference of these
craters um turns out between the um 185 kilm and 300 km diameter there's a
fundamental difference in in craters and many of them are now recognized to be
basins even though they're not 300 km in diameter and that is what happened to
deslandres deslandres turns out to be a basin as well so uh Bailey is a basin
desandre is a basin oh cool ta clavius has regained its status as largest
crater on the moon but hold the presses guess what glavius is also a basin it
has high gravity in the middle low gravity on the edges so clavius is now
classified as a basin but a crater so it's undergone quite a quite a change uh
you know the the EB and flow of how we understand the moon has uh kind of changed its its status but uh it it
remains a very impressive site in a in a telescope when you're looking at it
through a telescope you see the the southern limb of the Moon appearing there and you almost get this impression
you need to duck your head because you're in a spaceship zooming underneath the uh the southern part of the Moon and
U here we see cavus again and extending south from it uh uh these craters cadus
claproth and U um several others descending down and they look like
stepping stones heading south from clavius now these craters are 100 kilometers or more in diameter yet they
look small compared to clavus spanning uh 20 uh 25 uh well depending upon who
measures it U the US Geological Survey U gazeteer of uh planetary nomenclature um
says that it's 230 km in diameter uh the very popular lunar um charting program
virtual Moon atst says it's 225 I've measured it myself and plotting
it on um images U from Orbiter and through the U um um quickmap Tool uh
online where you get the digital elevation model you see all the elevations you know where the rim is I
come up with 221 kilm so depending upon the luck of the draw how your your your
two Crossways measurements land on the irregular Crater Rim uh you can come up
with a different figure by a kilometer or two every time so but all of my
measurements are within 70 excuse EXC me 97% of the USGS uh measurements so I'm
going to propose that yeah we're we're probably both right it's just the look of the draw of Where the Line crosses
the crater you you you you draw a diagonal x on it and measure one way measure the other way take the average
so if you spin that X around and land on different part of the rim it can vary by
a couple of kilometers so a crater diameter measurement is a kind of
imprecise uh because of the the rims are not
exactly round and the craters are not exactly uh um spherical they're they're
elliptical and uh another view of bananas and casadas and clao heading
south uh the the stepping stones and uh uh similar view just a a
rough and tumble territory down near the uh the South Pole of the Moon the southern
latitudes and another view featuring moretus uh the tyo look alike but here
we we see the the the the bottom limb of the Moon as we get closer and closer to
it here clavis we we see it you know we see its interior pretty good but the
closer to the pole that you get the more foreshortened it is so Moretta we can still recognize all of its features but
as you go further south further south further south here we're going we're we're marching down the the um series of
Newton craters um Newton a BC D um one
after another down here toward the uh the South Pole and they become more and more forh shortened where to the point
where you don't really recognize them anymore they're they're just Hills and bumps and uh the rims of the craters
making the mountain peaks along the moon but uh this one gouge this Valley right
here this is what leads to the lunar South Pole so an interesting place for
the emis astronauts that's their their Landing site high altitude view of it
getting close to the end of this um
uh see Tao kind of catches your eye because it's so fresh but uh clavus by
its sheer size uh deserves attention too
whoops yeah here we go um now this one kind of um illustrates why I say pavus
is almost like it was designed by an artist sculpted by a sculptor an artist
because we've got the Porter and Rutherford laying on its rims these are 51 and 55 kilometers in diameter large
craters on the moon but compared to clavus they look small then we've got this this series of satellite creators
arcing across the interior of it progressively larger and larger and larger and then finally coming down to
to Rutherford um almost like they were deliberately placed there by an
artist and some tourist shots all of these taken through my telescope up on
top of my garage here in in San Antonio and here we see the effects of libration
uh that's the effect of how the Moon kind of rocks back and forth and tips up and down a little bit because of its
elliptical and inclined orbit so sometimes clavius scoots a little closer to the
limb sometimes it's further away from the limb and here we see a a unfavorable
libration where clavius is about as far away far south as it can get uh all of
the territory that we were looking at earlier uh the the Stepping Stones they virtually disappear on the horizon where
earlier we could easily see them because the better libration angle and some parting views uh
sunset uh or Sunrise I mean uh U the Shadows from the East gives it a a
completely different personality than if the Shadows are
whoops I think I've skipped a slide by mistake here let's see there we go um
Shadows from One Direction yeah here we have the uh oh my sides are reversed that's a problem I'm supposed to show
the uh the East one first well here we see a West uh this is sunset on clavius
Shadows coming from the west and it gives it a different personality than what you would see uh when the sunrise
Shadows are coming from the other direction so uh Shadows on the moon play
a great deal in the character of the features that we look at uh the Shadows
can give them drama and uh um um you just a personality that's different as
the shadow shift from sunrise to sunset so um hope you've enjoyed my
little travel log here wonderful lvus the largest visible crater on the face
of the Moon and U maybe not a crater after all uh turns out it's a basin as
well so uh uh watch this space the moon's face is changing the map is not
static so uh uh let me uh stop share here and
whoops push the right button and it's been a lot of fun talking uh about the
moon again and uh hopefully um I U we can do something similar in the future
absolutely yeah looking forward to it um you know uh John Ray watching on YouTube
says to Caesar he says don't you know that lro stands for lunar Reeves
Orbiter oh that that would be fun that would be fun that would be fun if we could put our own satellite up there you
know the the photographic gear that we have nowadays we could probably build one you know a cube side or something
and uh hit your ride on one of one of the elon's Rockets headed up there who
knows sure okay well thank you so much Robert and uh we'll uh be looking
forward to having you on next time all righty thank you again thanks bye bye again okay um our next speaker is uh
marchello Souza marchello is uh uh professor and
Outreach uh educator extraordinaire uh he hails from Brazil and um he's live
with us now so thank you for coming on marchello
your Audi need to turn it up a bit it's just
low no is working is it working can you hear it's
working can you pick up the volume just a little bit I'm trying here it's getting
louder and always better there we go that's very good okay
now I changed the the mic I'm using a new camera now because this computer the camera is
isn't good a number of us have had computer problems this time so yes it's
a VGA camera I mean I bought a new one H I share my screen thank you very much
for the invitation Scott it's a great pleasure to be here thank you I share my
screen he it's very hot today now I am you can I don't know if you can hear a
background sounds it is the fun here because it's very hot here is more than
30 degrees now wow and we are near midnight and it's more than 30 degrees
it's very hot here in Brazil and I will show what we
are the activities we organized this last week and and also I will talk
about something that is special for us that is Carnival and I will show that is
associated with astronomy the carnival is totally associated with astronomy
this is the the new group that will be working in one school with
me astronomy project in a special group and we are beginning the development of
satellites setes as sit and this is the first step with this
group I hope soon have a new results that could s yes that is my one I hope
you soon have new results to show about this
project here is another school that say working 40 students from this school I
also is motivated to work with astronomy five sorry five students and I had a new
meeting with them today and this is at my University you
have a football field in in front of the the builds of the
university and at night we're having many lights around but it's possible to
use the telescope to take pictures and I had the opportunity to we have two days
with no clouds here and I stay during a long time there
and use the unella to make all the test and these are the pictures that I had
opportunity to take this is NGC
[Music] 5128 another one you see
293 and this that something sorry special because you probably you only
can see from the south hemisphere this
one that is in the Kina constellation NC
293 this is the SoMo Galax with a 12 minutes Exposition
time I call this but I know that they take pictures the telescope take pict
every four seconds and then process out theage but the total time of the process
was 12 minutes there's a picture of the Moon using this telescope that's a
fantastic and this is the Crab Nebula with 20 22 minutes
of and in the next day I was with a beach chair the chair that we use to go
to the beach here in Brazil yes because I stay for a long time there
and I was with a a Bach chair and I had
this m the m 100 this
NC 3628 that's part of the three plates of
Leo now with M 65 m66 this is M65
and this is the NGC 565 that is the call also AO that
you say in English the Nao Galax in Portuguese is the galaxy of the AA that
you use to to the fingers in the clothes and because it's very
th and this is the blacki Galaxy the m604 I'm trying to figure to take
picture of all the objects of the missia catalog that's possible to see here
during the night and I have most of then already I
took pictures of them and only the the
objects that are not visible here in the southem spere that I yet didn't take
pictures and this is now we have now the big holiday will begin Friday that is
our Carnival and you have everybody everybody no most of the
population be in the streets dancing this is what we see in most of
the cities in Brazil people dancing in the streets with music but what kind
what is is the association between Carnival and the astronomy I try to I
show now what you have in common because the date of the
carnival you you define every year using astronomy for this and I will show what
is the relations between astronomy and Carnival this is what we have as a
base the Pope Gregory 13 in the counil of n in
1582 defin the way to determine the date of the
E that is the main date that the Catholic Church
Define during the year and how that is defin the date of
the the OCC course Er When the first Sunday after
the full moon that occurs after the spring EO for you in the Northern
Hemisphere and for us here is the alumn eox the
fallox and for the Catholic church this date is fixed as March 21 but we can use
also the definition that you use in astronomy that works well also to Define this
days and if the day ER
happen this day the EAS if you use this after Beyond April
25 then Easter occurs uh Sunday before
previous Sunday and ER with this calculus the date of
the Easter Sunday happened ever between March 22
and the April 25 and now is the question the important question that use here what is
association with this that I'm say with the carnival is that because you need first
to choose the date of the Easter that you need to you need to know about de
nox the date of De nox and also the first full moon after thex and then the
Sunday after the full moon that happens after theox is the Easter and the
carnival you need to come back H turn from this
dates and where is the carnival here and about I'm say is this because the oh I
Chang something here what I did here something I move here sorry ah here then
uh you first choose the date of the Easter and then from the date of the
Easter you can Define the day of the as Wednesday that is when finish the
carnival for us here occurs 46 days before
Easter or you also can Define the date of the Sunday during the carnival that
is seven Sundays before 49 days before the Easter and this is the reason that
every year you have the carnival in different periods and something that
here in Brazil change everything because life here in Brazil
only is normal after the carnival the year for us begin in January but
everything here only works after caral the schools begin classes in February
but in reality everything work as we know during the
year only after the carnival then is very important for us and to define the carnival we need to follow the rules of
the Catholic church and it is associated with astronomy then every year we need
to and this year Carnival will begin this
Friday and here is date for this year then the AL OCC in March
20 and return the seventh Sunday before Easter and then you have the carnival
Sunday March 2 this that is important for us here
everybody's talking about Carnival here in Brazil and life return here only Monday
after the Monday Carnival March 10th that is the day that life turn here to
normal here in Brazil and this is another thing that
everybody was talking one week ago that's about the
asteroid the comments to 2024 why are for and they said that have
possibility to to hit the Earth but when they have more
dates you know that now they know that
it has not correct information and you don't have any risk of collision is near
zero now as something that every year you
have this information like this they first say that will be possible before
they analyze if out data and after this we know that for
luck for us it's a good luck for us that we don't have any risk coming from space
the risk is only the wars that you have here in your on the earth know and the
humans that are the problem on they are killing the others and for us the most
important event of the year will happen after Carnival then we
from the carnival and the next week we have the total lunar eclipse then have
feel time to to organize everything but we are working hard here to move to have
many people even it will happen during the night it'll be 2 am that you begin
here here for us but we are asking support of the police and everything to
stay in the streets in this Spirit to observe the eclipse I hope that the
weather help us because have this period is very hot then have days with no
clouds but have many days with clouds and rains strong rains and the
prediction for now is not we don't will not have strong RS I don't know one week
after Carnival what will happen but I hope we have conditions to observe these
fantastic events here and another way is also the
announcement of our international meeting that happen from 10 to 12 April
this year everybody that wants to participate you be very welcome it's only Insight event we don't transmit
life because we prefer to H continue
with the tradition to have the invited speakers in our city talking with the
students with the teachers with the general public here and we already have
confirmation of Alejandra Leon castella from Costa Rica edar cast from Guatemala
Alejandra from Uruguay that's director of dark sky artina Fern fabiani from
Uruguay that's director of dark sky in Uruguay Daniel Brito that is expert in
exoplanets here in Brazil and H fa that is expecting cosmology and this is what
are the list of the invited speak to now thank you very much for the invitation
ever is a great pleasure to be here after Carnival I I will be back
you'll be back after Carnival yeah where do where do people Park for Carnival I just see the streets
flooded with people many people goes with
bus have bus but many people use u in Brazil you have U tax every place they
go together and also you can go by car because you have place to stop the cars
they have parks that is not near you have walk but they go dancing and come
back from place you have safe placees to to park and to go but they walk it's no
problem they will be part they stay there for 12 12 hours 10 hours dancing
they begin during the night and finish in the morning you'll see many people that
sleep on the beach on yeah they they stay all night and stay on the beach and
then stay on the beach and then go home and no they stay again they just stay
wake up and go to dance again and stay out time I know many people that say
that only sleep after five days of the carnival so if I if I did some sidewalk
astronomy during Carnival I would probably have a lot of people looking at the yes a lot of drunk people there
have an eclipse that's happening during Carnival we organize an observation of a solar partial solar eclipse during the
carnival a lot of people was there to see wow wow I can imagine well thank you so much marel
it's a great pleasure thank you thank you so much um we will be moving on to
our next speaker here and uh let's see
um we've got um Dan Higgins uh for master World TV
Dan it looks like you're muted
Dan still muted all right go wonderful I thought
you controlled the mute I'm sorry no I only control the ass to unmute oh
it's it's been way too long I I can mute you but I wouldn't do that so I can M
Eric I wouldn't do that Eric mutes me all the time it's fine so how are things going at Astro World TV I know that you
you know you started your retail shop and and I think that's growing and getting better all the time and uh uh I
know you have a a wonderful loyal audience uh watching a Astro World TV
and uh you know you guys have shown so many people how to make great astrophotographs and uh you to really
get started in astronomy the right way so yeah no so um AST World TV uh just
went through its a nice little Milestone um Eric and I uh have just completed our
fifth year um of AST World TV and wonder yeah surpassed uh episode Eric what was
it four 400 was it 4 400 wow yeah four
400 was astop paloa 3 and if you miss it I'll show I'll show you real quick um
astop ploa 3 was an amazing event back in December and that was actually episode 400 um we do this thing it's
eight hours right
Eric is Eric muted
I'm sorry you we lose you you can't hear Eric no we can hear
you oh oh wow okay I don't know I'm not sure why okay um
interesting huh all right uh well
I don't want to I don't want to have dead air I apologize about that I know I know how that could be uh but but um uh
Hey I've had dead air myself so so I I mean c could you hear Eric now I'm sorry
Eric try and say something no I think maybe he has a
microphone problem no I could hear him it's just oh you can
okay oh that's that's interesting all right um
but anyway I Eric I'm sorry man I guess I guess you're you're down in the dumps
there so um I sorry man um it happens yeah well
everyone's having like issues today I don't know oh my goodness yeah we've had people get sick of the last minute um uh
you know computers crashing all kinds of stuff I I'm glad that my computer system stayed
online Eric is Eric's talking I think I know yeah how about
how about now Eric go ahead speak uh I think so there we go
there I got got I'm gonna let you guys have the uh have the stage here I gotta so I apologize about that that was me it
was all me okay but um yeah so Eric you know um so we've
been doing what five years doing this yeah we could all hear you yeah okay cool there we
go beautiful awesome so yeah so we've been doing this as pla it's like it's
like eight hours right so we had yeah yeah do we have on this year that's a
long schedule uh well you know this year we've had you know we had Trevor this
year we had um weedos um yeah weo or we
had we Orman from weo Asal Forum um we've had uh of course we've had um you
know Sarah Matthews with from Sarah's astrom maath which is she's been fantastic we've had um Wayne Parker and
um and um Shan neelen as well as um you know gosh there was just so
many Molly Wakeling was again this year yes yes Molly Wakeling
absolutely Y and uh Ben Ben from the Nar band Channel and uh yes can't forget the
uh the masters of pxs insight and Simon Tang either so sure oh yeah Simon Tang
he was awesome you know sharing us a lot of information and um giving us a bit on on um solar and
everything it was you know it was an awesome it was an awesome time we had a great time yeah we we nuts we do it the
first set Saturday in December but um you know we we're up to episode like 420
or so now um and uh looking to looking to break a half a half a thousand um
this year hopefully so uh so we'll see how that works out so yeah um yeah and
Derek you you launched your website too right you're as with Eric yes yeah it's been it's been about
a year now that I've launched Astro with Eric and for anyone who is thinking
about a doing a website you know for their actual photography or anything
like that it's a it's it's it's a great thing to do but it's also it's also a
challenge you know trying to keep up with everything it's a great repository for all of my Imaging but I've also
tried to do blogs every once in a while um but with real life and now I've had
this big you know family move um to Southern um to to the Southern United
States to Georgia it's been kind of hard to keep up with everything but but yeah it's just been uh that's all that's
that's been a great thing to do is um so I highly encourage you you know if you're interested in doing a website for
your astrophotography and everything like that to go for it um there's some work put into it but it's it's worth it
all the end yep I mean it's it's been great for you and you got some real great pictures
on that so if you're if you're just sub butting as photographer or just looking for some ideas go hit up uh Eric's
website because he's got some good stuff going on there um yeah yeah for sure it's it's it's pretty cool so thanks
yeah it's um like I said it's it's some good stuff and we we also
celebrated uh the second year of AST World telescopes retail store um so this
is uh the beginning of year to so that is awesome and that's that's been a
crazy ride itself as well you know your dream that's been for you know something
he wanted to do for such a long time yeah I'm I'm well I'm hoping you know you know it's still you know it's still
that that that's definitely a challenge it's definitely a challenge um starting it coming out of covid um and then
trying to keep it going and uh and uh it's it's doing well we'll be at Nee again this year we'll have uh all I
believe all three of us you me and Dave the three hosts for as World TV will be
there um right next to primu right in the main row we're right there we both
got two tables um so uh we we I tried to get PR luch to buy two and a half tables
to take the whole row but they wouldn't go for it so uh but uh but but it it's
been a lot of fun this will be uh the third Neath that we are a first one was
really just for the show the second NE that we were out um we opened up the
store and then this will be we're going to have a lot of product there so come see us um it's
only what is it five six weeks away so yeah yeah it's not yeah it's right
around the corner you know it's what first that first what first two weeks of April fth six right yeah so fth six yeah
first week of April so yeah it's not that far away yeah so come check us out
and uh hang out with us and we'll have a good time
so wonderful well great uh is that
um any other news any other things you'd like to share before we call it a
night um no just if anybody out there wants to be a guest um on our show and
uh do another presentation I know we've had a bunch of people from um Global
Star Party to come on uh we had Adrien Bradley we had yourself we had Maxi
Fades um so there a lot of us a lot of them came on so they do a great great
great presentations and great as photographers so wonderful all right and what's your website once again we're
lucky we're gonna have a local Georgia astronomer um who has done a lot of Articles within um sky and Telescope um
uh Dan um lellan uh he's going to be coming on oh yeah very soon we've agreed
with him um so we just need to schedule that he's going to be talking a lot about planetary as well as deep sky but
we're going to be focusing a lot on planetary because that's what our audience members have been asking a lot about is about planetary and doing
planetary Imaging and things like that I even have you know struggles with planetary because it's a whole different
Beast than deep sky so having the opportunity to have a person of his you
know of his years he's been doing this for 20 24 25 years and like I said and being able to publish you know his
articles in sky and Telescope having somebody of that caliber it's GNA be pretty it's gonna be pretty cool yeah
but uh yeah if you want to get some more information like Scott was alluding to um uh about the website if you want some
information about Astor or Astor telescopes you go to um AstroWorld
web.com and that's for the TV show they didn't have Aster World TV it was stolen by Travis Scott so I couldn't take um
and and if you want some uh if you want if you want to shop at our store you can go to Astor telescopes.com and you could
uh we have all all of your favorites from explore scientific all the way up to player one and uh whoever else is out
there we got everybody so wonderful wonderful well all the luck to you guys
and um you guys should tune in to AstroWorld web.com I've put up the links
and uh of course the link to AstroWorld telescopes.com these guys will treat you
right and teach you everything you need to know uh so and and that's something
that is uh hard to come by you know is to get a lot of expertise you know you can't
you know there's there's uh there are websites U uh you know that you can go
to where you can buy the the product but if you can't get the service and the
knowledge and all the rest of that stuff it's because there's a lot to learn about uh about your product and you want
to buy from experts like uh like these guys so yeah it's definitely one of the
things that I'm hearing you know and I'm sure you hear the same same thing Scott about you know I get my telescope from X
and well not X but you know get get my telescope from somebody I can't talk to anybody because
they have no idea yeah they don't know what it is so um yeah the transaction
but they don't know what it is so it's kind of like buying diving gear and you want to go diving and uh they sell you
everything you can't ask anyone at the place where you bought the diving gear from it kind of leaves you with a
feeling like did I buy the right stuff or you know or could I bought better
stuff you know uh you know so it's definitely a challeng in those terms
because it's it is your lifestyle it is your valuable time and you want to make
the best use of that you know so you want to buy from experts if at all possible absolutely at least somebody
you can get on the phone that's very true that too that too that too well
thanks very much guys and I want to thank the audience uh tonight um I want
to give a special thanks to uh Dr fella terenzi for inviting the uh Florida
International University student students to tune in uh tonight and um um
you know uh everyone that was able to make it and those that weren't able to
make it tonight uh I know that you um I know that you tried and so we'll have
you on another Global star party and um we'll be posting that information soon
so have a good night and uh keep looking up guys take care take
[Music] care all right we're good
right I could hey Dan I could not hear I could not hear
him [Music]
[Applause] [Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
[Music]
w
[Music]